Figure 5.
NuRD Is a General Regulator of Transcriptional Heterogeneity
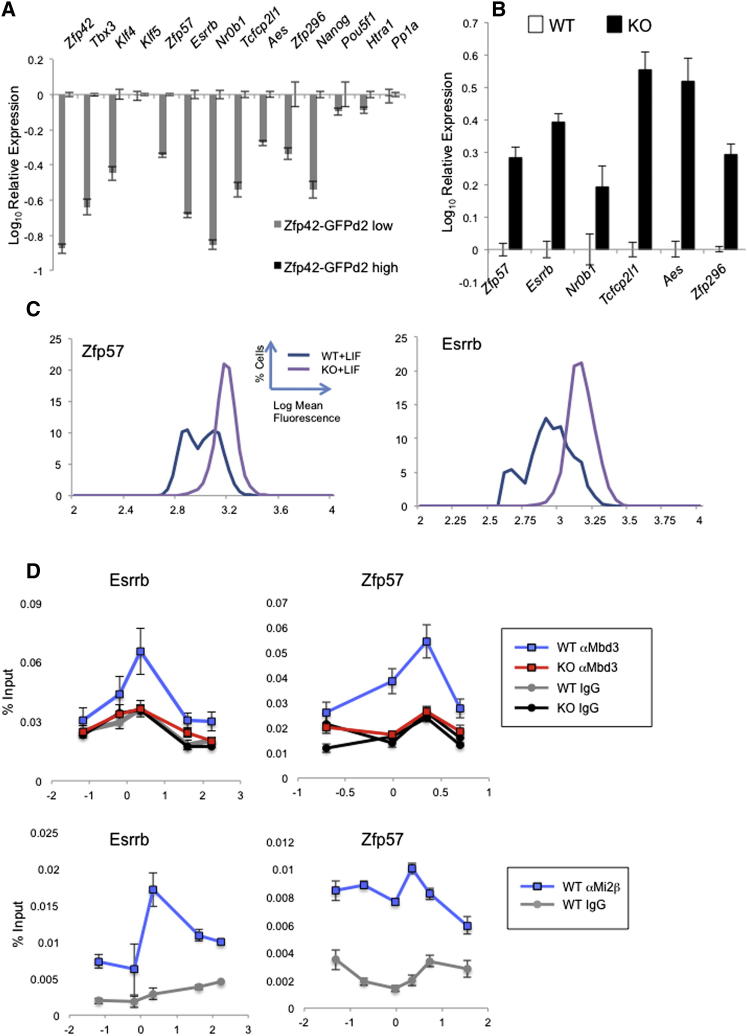
(A) Gene expression in Zfp42-GFPd2-low cells is expressed relative to expression in Zfp42-GFPd2-high cells (Marks et al., 2012). Included are genes identified by bioinformatic analysis (Zfp42, Tbx3, Klf4, Zfp57, Esrrb, Nr0b1, Tcfcp2l1, Aes, and Zfp296) as well as control pluripotency-associated genes (Klf5, Nanog, and Pou5f1) and one gene shown to be subject to NuRD-dependent transcriptional silencing in ESCs but not display transcriptional heterogeneity (Htra1; Reynolds et al., 2012). The latter two sets of genes do not display transcriptional heterogeneity in this assay. Ppia is a control housekeeping gene.
(B) Expression of indicated genes in Mbd3−/− ESCs expressed relative to levels in wild-type ESCs.
(C) Expression analysis for Zfp57 and Esrrb in wild-type (WT) and Mbd3−/− (KO) ESCs in serum and LIF conditions as in Figure 3A above.
(D) ChIP was performed with anti-Mbd3 (top panels) and anti-Mi2β antibodies (bottom panels) as well as control IgG antibodies across the transcription start sites of Esrrb (left panels) and Zfp57 (right panels) in wild-type (WT) or Mbd3−/− (KO; anti-Mbd3 ChIP only) ESCs grown in serum and LIF conditions. Immunoprecipitates were probed with primer pairs located across the indicated gene promoters and plotted as percentage of input (y axis). Numbers along the x axis indicate distance relative to major ES transcription start site for indicated genes in ESCs.
See also Table S1.