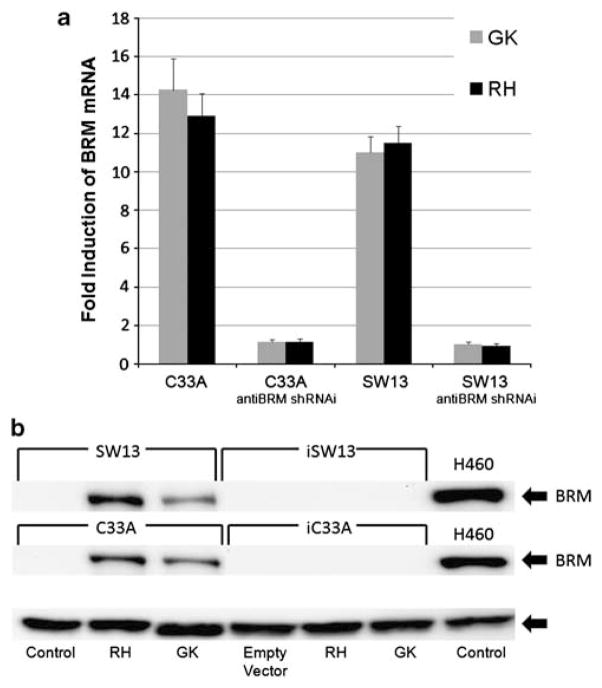
Figure 1.
Pharmacological induction of BRM. (a, b) Induction of BRM pharmacologic application of compounds, RH and GK (Maybridge Trevillett, Tintagel, Cornwall, UK). Error bars reflect standard error of experiments repeated at least six times. (a) RNA was collected using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and isolated using Qiagen’s RNeasy kit, as per manufacturer’s instructions (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA). Complementary DNA was generated from 1 μg of DNase-free RNA using iScript (BioRad, Hercules CA, USA), as per manufacturer’s instructions. Real-time reverse transcriptase PCR was performed using RT Fast SYBR Green/ROX qPCR Master Mix (SABioscience, Valencia, CA, USA), with the following conditions: 95 °C, 10 min; 40 cycles (95 °C, 10 s and 60 °C, 30 s). Induction of BRM mRNA by the application of RH or GK for 72 h, measured by quantitative PCR, on the BRM-deficient C33A and SW13 cell lines. In the controls, anti-BRM shRNAi-infected SW13 and C33A daughter cell lines, BRM was not induced. Polr2A was used as the control for these experiments. (b) Cell lines were grown in RPMI with 5% fetal bovine serum supplemented with Pen/Strep and Glutamax (Invitrogen). These cell lines were authenticated by sequencing the p53 mutations and K-ras mutations in each cell line used compared with published results. C33A and SW13 cells were treated for 120 h with RH (50 μM) or GK (200 μM) and protein was isolated (Glaros et al., 2007). To perform western blot analysis, 80 μg of protein was used (Strobeck et al., 2002; Reisman et al., 2002, 2005). BRM expression was detected using polyclonal anti-BRM antibody, previously described in (Glaros et al., 2007), chemiluminescence (Amersham GE Healthcare, Piscataway, NJ, USA), and normalized to GAPDH expression (Trevigen, Gaitherburg, MD, USA). Induction of BRM protein by western blot analysis after the application of either GK or RH for 6 days. GAPDH was used as the loading control.