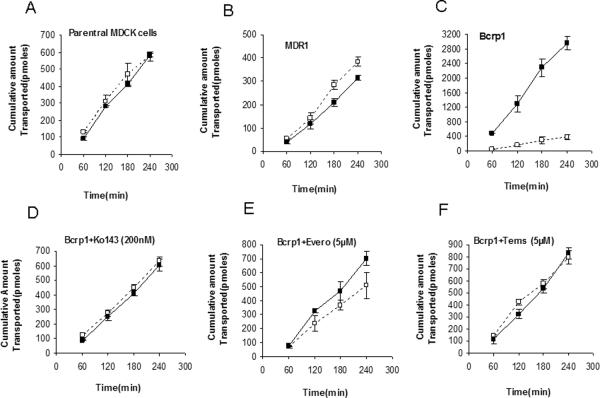
Fig.2.
Transepithelial transport of vandetanib (5μM) across MDCKII cell monolayers. Bi-directional transport was carried out in MDCKII parent (A), MDR1 (B) and murine Bcrp1(C) transfected cell monolayers. Significant directionality of transport was observed in Bcrp1 transduced MDCKII cells, this net flux was abolished upon preincubating 200nM Ko143 (D), a specific Bcrp1 inhibitor. Also, everolimus and temsirolimus (E and F) were both equally potent (at 5μM), to eliminate the directionality of vandetanib flux. ( ); translocation from apical-to-basolateral chamber, (
); translocation from apical-to-basolateral chamber, ( ), translocation from basolateral-to-apical chamber. Results are expressed as Mean±S.D. n=3 wells.
), translocation from basolateral-to-apical chamber. Results are expressed as Mean±S.D. n=3 wells.