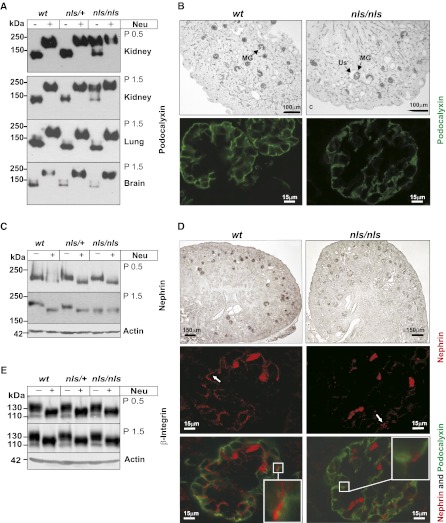
Figure 6.
Kidney-specific sialylation analysis of distinct proteins in nls/nls mice. (A) Podocalyxin immunoblot of total lysates from P0.5 and P1.5 organs of all genotypes before (−) and after (+) removal of sialic acids by neuraminidase (Neu) treatment. (B) Immunostaining of podocalyxin in paraffin-embedded kidney sections of wt and nls/nls mice analyzed by light microscopy (upper panel) and fluorescence staining of podocalyxin (lower panel, green) in P1.5 wt and nls/nls kidney paraffin sections analyzed by confocal microscopy. MGs were stained positive for podocalyxin, whereas ureteric buds, renal vesicles, or comma-shaped bodies remain unstained. (C) Nephrin immunoblot of total kidney lysates at P0.5 and P1.5 before (−) and after (+) Neu treatment. (D) Immunostaining of nephrin in paraffin-embedded kidney sections of wt and nls/nls mice analyzed by light microscopy (upper panel), fluorescence staining of nephrin in red (middle panel), and fluorescence double staining (bottom panel) of podocalyxin (green)/nephrin (red) in P1.5 wt and nls/nls kidney paraffin sections analyzed by confocal microscopy. Selected areas are shown with larger magnification in white boxes. Nephrin dots are marked with white arrows. Erythrocytes are stained unspecifically. (E) β1-integrin immunoblot of P0.5 and P1.5 untreated (−) or Neu-treated (+) kidney lysates. Actin is the loading control. Us, enlarged urinary space.