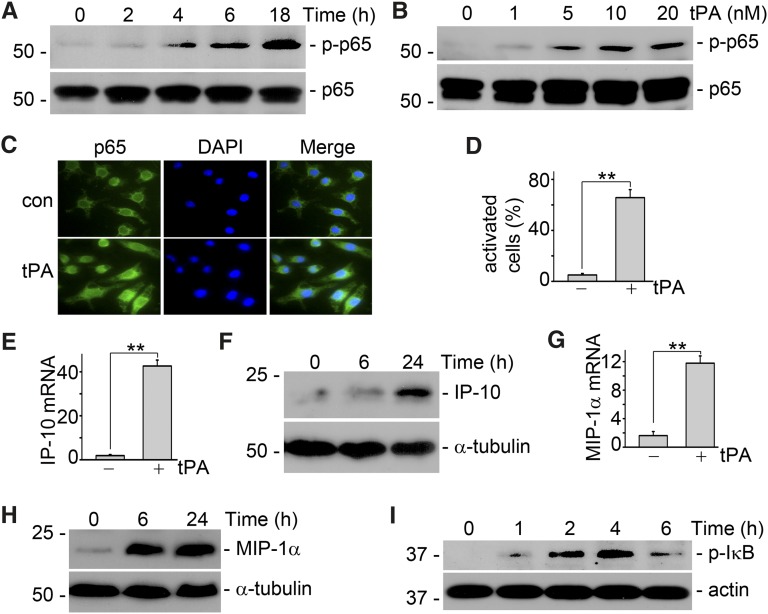
Figure 1.
tPA activates NF-κB pathway in macrophages. (A) J744 macrophages were treated with 10 nM tPA for 0, 2, 4, 6, and 18 hours. Western blot showed that tPA induced phosphorylation of p65, a classic marker of NF-κB activation, as early as 4 hours. (B) J774 cells were incubated with 0, 1, 5, 10, and 20 nM tPA for 6 hours followed by Western blot for phospho-p65 and total p65. (C) Macrophages were incubated with vehicle or 10 nM tPA for 6 hours followed by immunofluorescence staining with anti-p65 antibody and DAPI. Original magnification, ×400. (D) Quantitative illustration of tPA-induced p65 nuclear translocation in J774 macrophages. Unit was expressed as the number of macrophages with p65 nuclear translocation per 100 cells. **P<0.01 (n=3 experiments). (E). Macrophages were treated with vehicle or 10 nM tPA for 6 hours followed by quantitative PCR assay for chemokine interferon-inducible protein-10. **P<0.01 (n=3). (F) Interferon-inducible protein-10 protein level was determined by Western blot. Macrophages were incubated with 10 nM tPA for indicated periods. (G) Macrophage-inflammatory protein-1α mRNA level was evaluated by quantitative PCR assay after treatment with 10 nM tPA for 6 hours. **P<0.01 (n=3). (H) Macrophage inflammatory protein-1α protein level was assessed by Western blot. J774 cells were treated with 10 nM tPA for 0, 6, and 24 hours. In the cases to determine the cellular protein level of chemokines, J774 macrophages were incubated with Brefeldin A solution (eBioscience, San Diego, CA) 5 hours before harvest to blockade the releasing of chemokines from the cells. (I) tPA induced phosphorylation of IκB, a marker of canonic activation of NF- κB, as indicated by Western blot analysis.