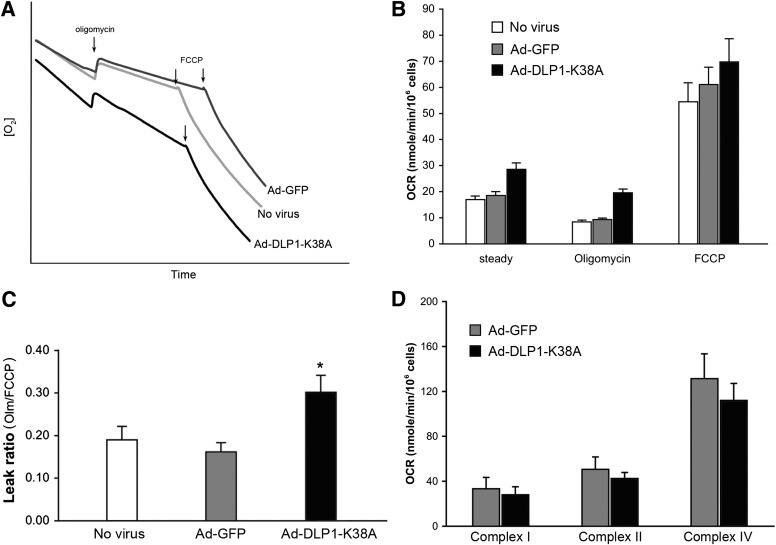
FIG. 3.
Expression of DLP1-K38A induces the mitochondrial inner membrane proton leak. A: An oxygraph shows increased respiration by cells expressing DLP1-K38A. B: Calculated OCR indicates that cells expressing DLP1-K38A have higher rate of oxygen consumption in the steady state and in the presence of oligomycin. The maximum OCR in the presence of FCCP shows no significant difference between control and DLP1-K38A cells. Error bars represent SEM. Results are n = 12. P < 0.005 at the steady state and with oligomycin comparing with Ad-GFP-infected cells. C: The leak ratio is presented as the ratio of the OCR with oligomycin to the maximum OCR (OCROligomycin/OCRFCCP). The leak ratio is significantly higher in DLP1-K38A cells. Error bars are SEM. *P < 0.01 with Ad-GFP and *P < 0.05 with uninfected control. D: Respiration of semi-intact cells to evaluate individual complex activities. Glutamate/malate, ADP, rotenone, succinate, antimycin A, and TMPD/ascorbate/cytochrome c were sequentially added to digitonin-permeabilized cells for OCR measurements. Relative activities of complex I, II, and IV between Ad-GFP and Ad-DLP1-K38A cells were compared by the OCRs after adding glutamate/malate/ADP, succinate, and TMPD/ascorbate/cytochrome c, respectively. Results are n = 3 for Ad-GFP and n = 5 for Ad-DLP1-K38A.