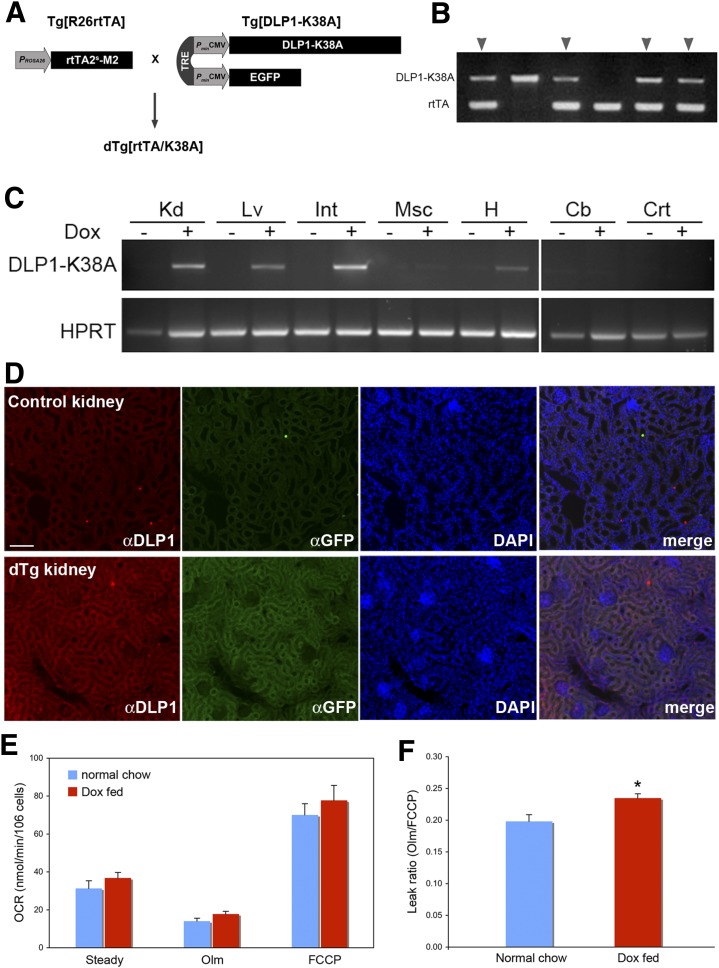
FIG. 6.
New transgenic mouse model expresses DLP1-K38A. A: The double transgenic mice dTg[rtTA/K38A] were generated by crossing Tg[R26rtTA] and Tg[DLP1-K38A]. DLP1-K38A and EGFP are cis-regulated by TRE and trans-regulated by the Dox-dependent transcription factor rtTA2s-M2 that is under the control of the ROSA26 promoter. B: Transgene genotyping of a litter showing double transgenic mice carrying both DLP1-K38A and rtTA (arrowheads). C: Dox-dependent expression of DLP1-K38A in dTg[rtTA/K38A]. RT-PCR of tissues from 2-day Dox-fed mice shows the DLP1-K38A expression in kidney (Kd), liver (Lv), small intestine (Int), and heart (H). Little expression was detected in muscle (Msc) or in brain cerebellum (Cb) and cortex (Crt). D: Immunohistochemistry on the Dox-fed dTg[rtTA/K38A] kidney section shows increased levels of DLP1 and GFP. Scale bar: 25 μm. E: OCR analyses of hepatocytes from chow and Dox-fed dTg[rtTA/K38A]. Transgene expression was induced 4–5 days, and OCR was measured 2 h after hepatocyte isolation. Olm, oligomycin. F: The leak ratio indicates a statistically significant increase of proton leak in Dox-fed dTg[rtTA/K38A] (n = 15 for Dox-fed; n = 11 for normal chow-fed mice). Error bars represent SEM. *P < 0.01. (A high-quality digital representation of this figure is available in the online issue.)