Fig. 5.
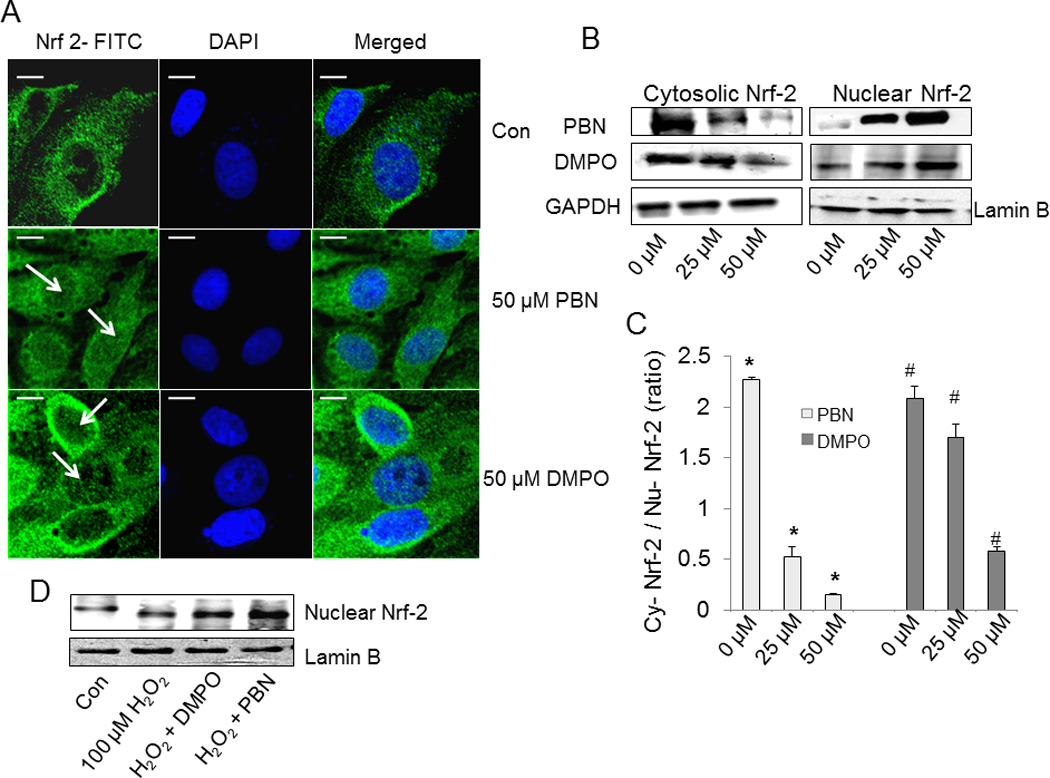
Effect of nitrones on nuclear translocation of Nrf-2. (A) BAEC were treated with nitrone (0–50 µM) for 24 h. After treatment, cells were immunostained with goat polyclonal anti-Nrf-2 antibody (1:200 dilutions) followed by anti-goat FITC-conjugated IgG antibody (1:150 dilutions) and DAPI (1 µM) to stain the nucleus. After incubation, cells were washed with PBS and images were taken by Olympus FluoView-1000 confocal microscope at 60 X magnification. The right panel corresponds to the merged image of FITC-fluorescence and DAPI-fluorescence, bar represents 10 µm. The figure represents the best of three independent experiments (n = 3) (B) Western blot analysis of the cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts of nitrone-treated BAEC, using anti- Nrf-2 primary antibody (1:500 dilution). Anti-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (1:1000 dilution) and anti-lamin B (1:1000 dilution) antibodies were used as loading controls for the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions. The figure represents three independent experiments (n = 3) (C) Densitometric ratio of cytosolic vs. nuclear Nrf-2 in nitrone-treated BAEC, calculated from the respective band intensities. Data are represented as the mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05 vs. control (PBN-untreated cells) and #p < 0.05 vs. control (DMPO-untreated cells), where n =3. (D) Immunoblot analysis of the nuclear extracts of untreated, H2O2-treated, and nitrone-preincubated H2O2-treated BAEC for Nrf-2, using anti- Nrf-2 primary antibody (1:500 dilution) and anti-lamin B (1:1000 dilution) as the loading control. The figure represents three independent experiments (n = 3).
