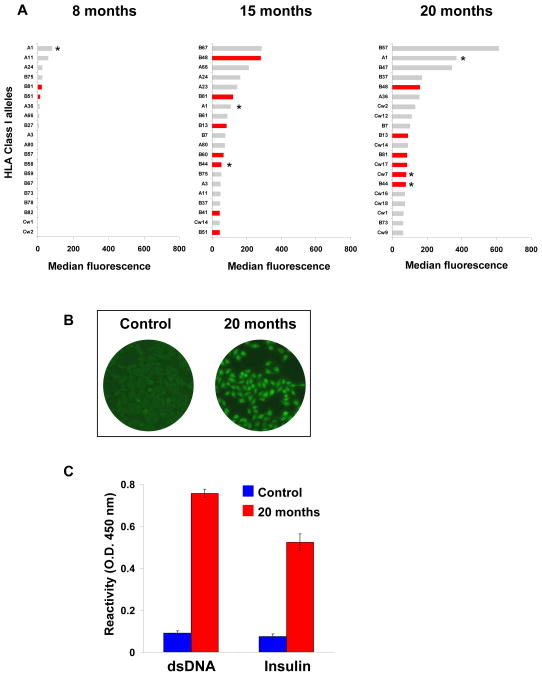
Figure 5.
Patient’s serum reactivity. (A) The reactivity of the patient’s serum IgG to HLA class I molecules was tested by Luminex. The 20 alleles towards which the serum was most reactive are depicted for 3 time points post transplantation. Class I alleles towards which clone 4G10 was most reactive are depicted as red bars. Class I alleles expressed by the donor are labeled with an asterisk. (B) The patient’s serum IgG reactivity to Hep-2 cell was determined using a sample collected at time of transplant nephrectomy (20 months post-transplant). The serum of a representative non-CHR patient was used as control. Staining was revealed using a FITC-conjugated anti-IgG secondary. (C) Serum reactivity to self antigens. The patient’s serum collected 20 months post-transplantation was assessed for reactivity to dsDNA and insulin by ELISA. A serum sample collected from a non CHR patient was used as control. The reactivity was revealed using an HRP-conjugated anti-IgG secondary antibody.