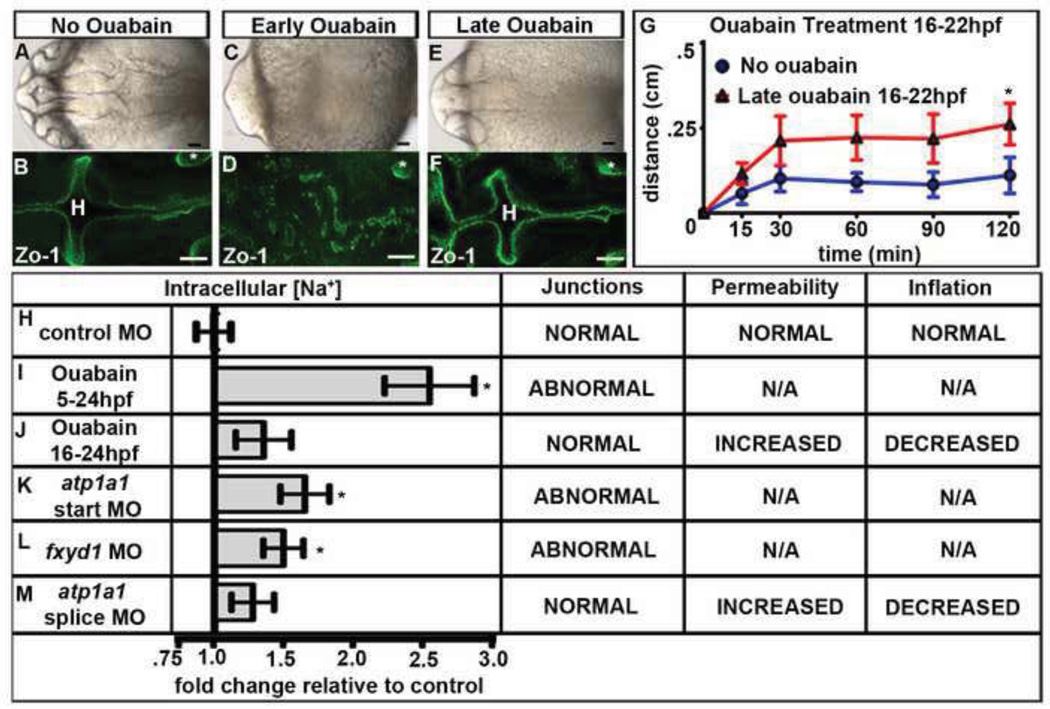
Fig. 3. Na,K-ATPase pumping is required for brain ventricle development.
(A–F) Wild type embryos either untreated (A–B) or ouabain treated from 5–24 hpf (early; C–D) or 16–24 hpf (late; E–F). Brightfield dorsal (A,C,E) or Zo-1 (B,D,F) images. (G) Dye retention assay in untreated (red) vs. late ouabain treated (blue) embryos. Data represented as mean +/− SEM. * = p<.05 compared to control. (H–L) Quantification of fold changes in [Na+]i and corresponding brain ventricle phenotype. Data from 3–8 independent experiments represented as fold change compared to control MO (equal to 1) plotted as a mean +/– SEM. *=p<0.05 compared to control. All embryos at 24 hpf, anterior to left; Asterisk = ear, H = hindbrain. Scale bars = 50µm.