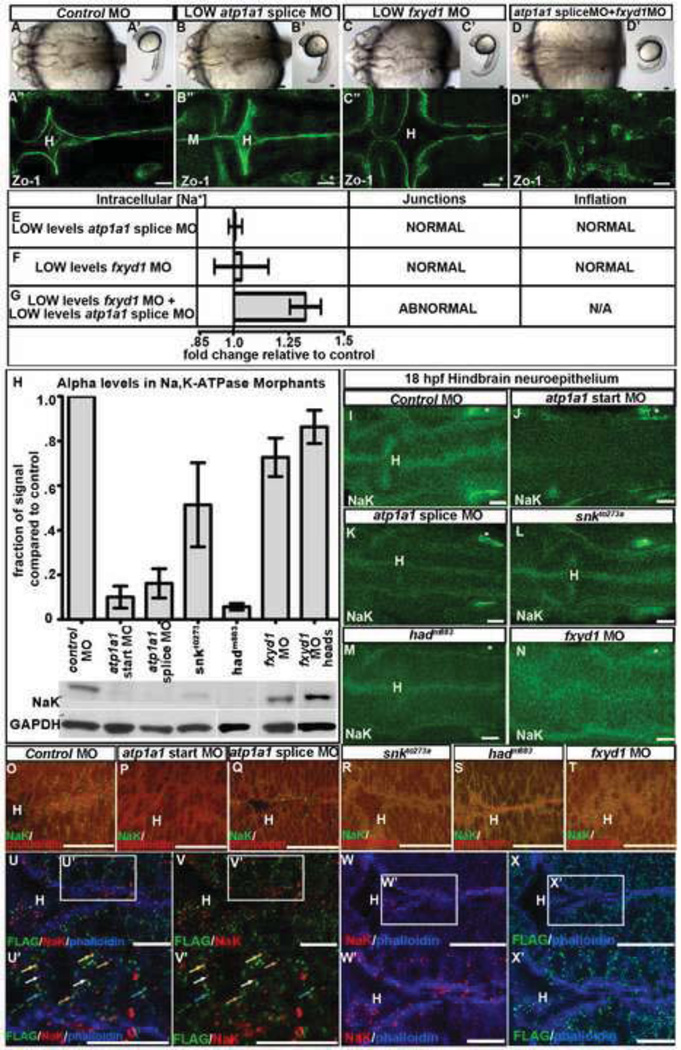
Fig. 4. Atp1a1 and Fxyd1 synergy, interaction and colocalization.
(A–G) Atp1a1 synergizes with Fxyd1. Brightfield dorsal (A–D), lateral (A’–D’) and Zo-1 staining (A’’–D’’; different embryos imaged than A–D) and measurement of [Na+]i with corresponding brain ventricle phenotype (E–G), in control (A), low atp1a1 splice MO (B,E), low fxyd1 MO (C,F) or together (D,G) at 24 hpf. Data representative of 3–6 experiments as fold change relative to control = 1; mean +/− SEM. (H) Western quantification of Atp1a1 (NaK) in 24 hpf whole embryos normalized to GAPDH. Representative of 3–4 independent experiments; mean +/− SEM. (I–T) Atp1a1 (NaK) in 18 hpf control MO (I,O), atp1a1 start site MO (J,P), atp1a1 splice site MO (K,Q), snkto273a (L,R), hadm883 (M,S) and fxyd1 MO (N,T). NaK alone (I–N, green) or with phalloidin (O–T, actin, red). (U–X) Localization of Atp1a1 (NaK; red) and Fxyd1-FLAG (green), phalloidin (blue) in fxyd1 MO embryos rescued with fxyd1-FLAG overexpression and imaged at 24 hpf. (U’–X’) Higher magnification indicated by box in (U–X). Co-localization (yellow arrow), adjacent (orange arrow), Atp1a1 alone (white arrow) and Fxyd1 alone (blue arrow). Anterior to left. Asterisk = ear. H = hindbrain. Scale bars = 10µm (U–X), 50µm (A–T).