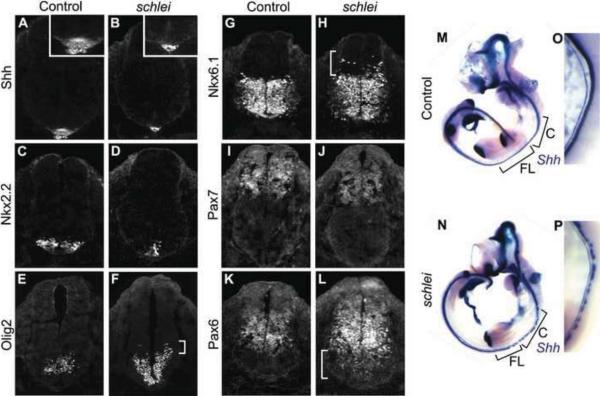
Figure 2. schlei mutants show disruptions in ventral cell type specification and neuronal subtype mixing in the neural tube.
Sections through e10.5 neural tubes reveal that the floorplate is lost (A,B) and other ventral cell types including V3 interneuron progenitors (Nkx2.2+; C,D) are decreased in number and specified at more ventral locations than in wild type. Cells requiring intermediate levels of Shh signaling, such as motor neuron progenitors (Olig2+; E,F), are both specified more ventrally and expanded dorsally (bracket in F) in schlei. Other intermediate cell types, including a population marked by Nkx6.1 (G,H), are also expanded dorsally in the mutant and are mixed with more dorsal cell types (bracket in H). Some dorsal cell populations, such as the region demarcated by Pax7 expression, appear unchanged in schlei mutants (I,J). In contrast, Pax6 expression, which in wild type embryos (K) is inhibited by high levels of Shh, expands ventrally in schlei (bracket in L). The loss of the floorplate varies based on the axial level as visualized by whole mount in situ hybridization for Shh, with gaps in expression found particularly at the cervical and forelimb levels (M,N). (O,P) Higher magnification views of the cervical regions in e10.5 embryos highlight gaps in floorplate expression of Shh in schlei mutants. C; cervical; FL; forelimb. Control and schlei mutant images are shown at the same magnification.