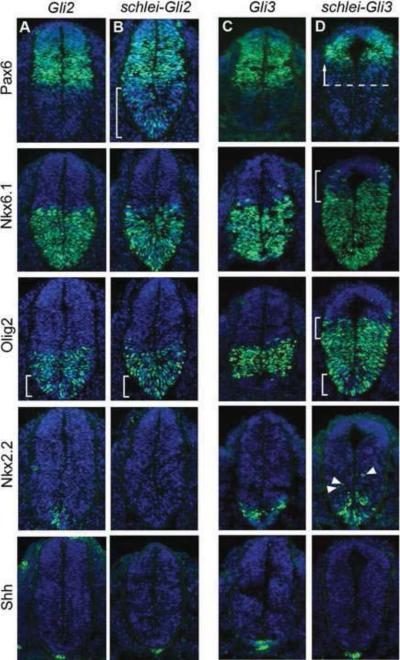
Figure 4. schlei interacts genetically with Gli3 and Gli2 to pattern the ventral and intermediate neural tube.
e10.5 neural tubes stained for DAPI (blue) and neuronal markers (green). Expression of Pax6 is similar to wild type in Gli2 (A) and Gli3 (C) mutants, but the ventral border is extended ventrally in schlei-Gli2 (B, bracket), consistent with the schlei single mutant. In schlei-Gli3 embryos, there is a strong dorsal shift in the ventral border of Pax6 (D, arrow). The dorsal expansion of the Nkx6.1+ population observed in schlei is exacerbated in schlei-Gli3 (bracket) but rescued in schlei-Gli2. While intermediate cells such as Olig2+ motor neuron progenitors are comparable to wild type in Gli3 mutants, they are specified more ventrally in Gli2, schlei-Gli2, and schlei-Gli3 (brackets). Additionally, the dorsal boundary of expression of Olig2+ is pushed even further dorsally in schlei-Gli3 (upper bracket) than in schlei, but in schlei-Gli2 is restored to a level similar to wild type. Nkx2.2+ V3 progenitor cells are reduced in number and specified more ventrally in Gli2 mutants, but are completely lost in schlei-Gli2 double mutants. Nkx2.2+ cells are normal in Gli3, but are specified more ventrally and dorsally (arrowheads) in schlei-Gli3 double mutants. The floorplate, as marked by Shh, is normal in Gli3 but is absent in schlei-Gli3, Gli2, and schlei-Gli2 despite normal Shh staining in the notochord, similar to schlei mutants. All neural tube sections are shown at the same magnification.