Fig. 2.
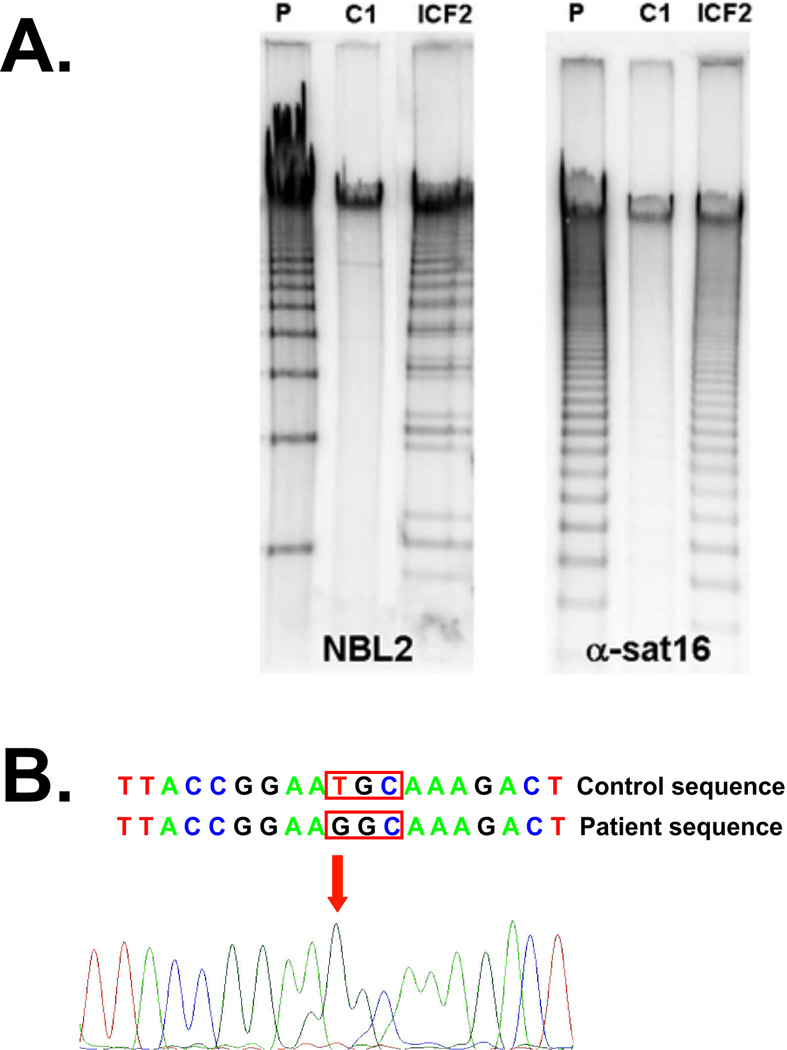
A. Southern blot analysis of the NBL2 and α-satellite was performed in the present patient (P), in his father (C1), and in a confirmed ICF2 patient (ICF2) with a known nonsense mutation in ZBTB24 gene (p.R320X). DNA samples (4 µg) were digested overnight with the restriction enzyme EcoR52I (NBL2) or HhaI (α-satellite), separated by linear gel electrophoresis on a 0.8% agarose gel and transferred on a nitrocellulose membrane, which was hybridized with probes targeting the NBL2 or the α-satellite repeat on chromosome 16. B. Sanger sequencing of coding exons of ZBTB24 revealed a homozygous missense mutation (c.1222T>G, p.408C>G).