Figure 4.
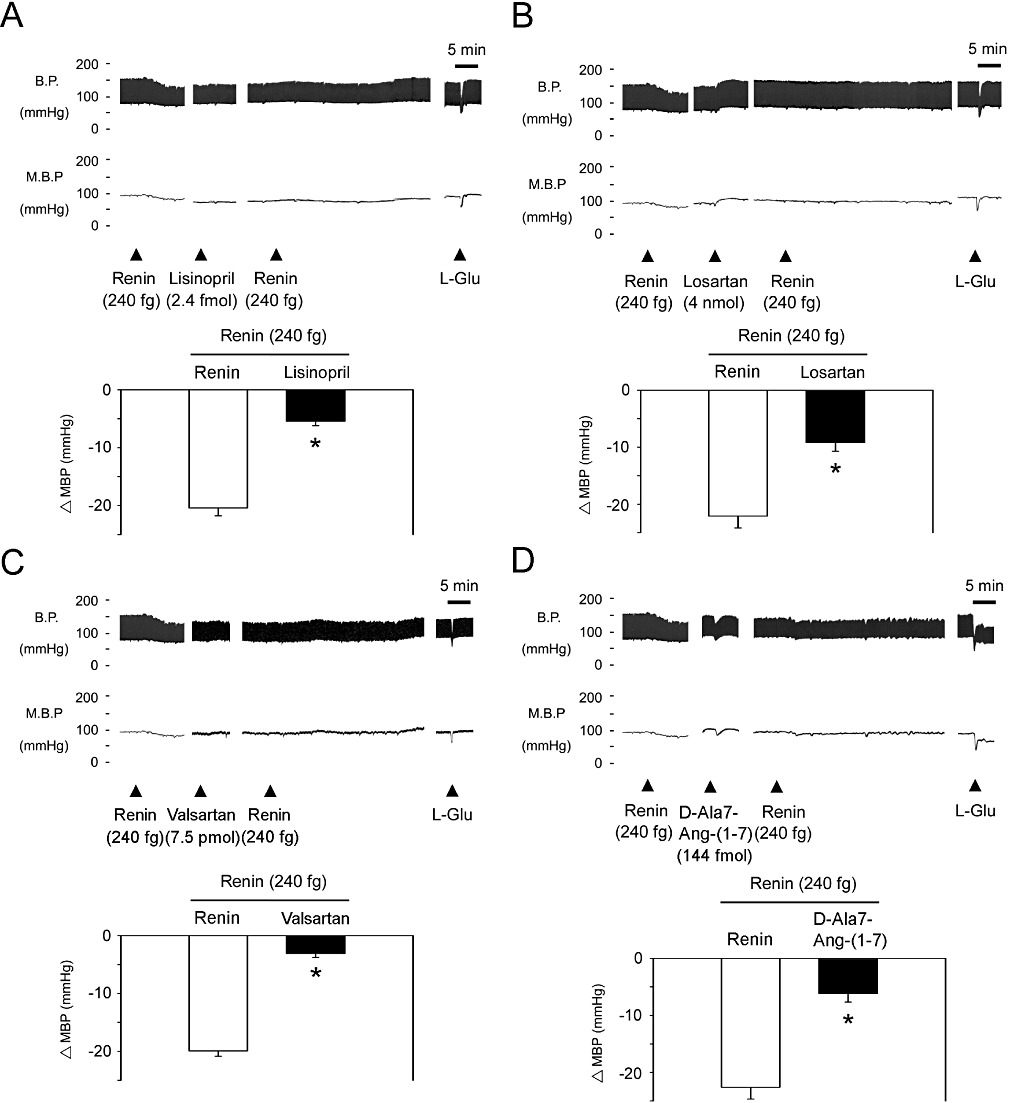
Angiotensin AT1 and Mas receptors participate in renin-mediated depressor effects at the NTS. (A) Blood pressure response to renin (240 fg) injection into the NTS after administration of the ACE inhibitor, lisinopril (2.4 fmol). Representative tracings demonstrate that the depressor effect of renin was significantly attenuated by lisinopril. Summary data (means ± SEM, n= 6) are shown in the graph. *P < 0.05, significantly different from the renin group. (B) Blood pressure response to renin (240 fg) injection of into the NTS after administration of losartan (4 nmol). Representative tracings demonstrate that the depressor effect of renin was significantly attenuated by losartan. Summary data (means ± SEM, n= 6) are shown in the graph. *P < 0.05, significantly different from the renin group. (C) Blood pressure response to renin (240 fg) injection of into the NTS after administration of valsartan (7.5 pmol). Representative tracings demonstrate that the depressor effect of renin was significantly attenuated by valsartan. Summary data (means ± SEM, n= 6) are shown in the graph. *P < 0.05, significantly different from the renin group. (D) Blood pressure response to renin (240 fg) injection of into the NTS after administration of the angiotensin-(1-7) antagonist, D-Ala7-Ang-(1-7) (144 fmol). Representative tracings demonstrate that the depressor effect of renin was significantly attenuated by D-Ala7-Ang-(1-7). Summary data (means ± SEM, n= 6) are shown in the graph. *P < 0.05, significantly different from the renin group.
