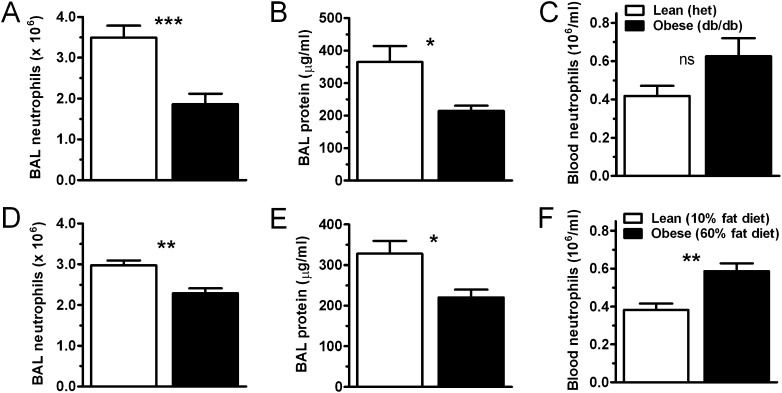
Figure 1.
Obesity attenuates airspace neutrophilia and lung injury in db/db and diet-induced obese mice. Acute lung injury was induced by the inhalation of LPS in genetically obese (db/db) versus lean (heterozygous littermate control) mice (A–C), and diet-induced obese (60% fat diet) versus lean (10% fat diet) mice (D–F). Mice were exposed to nebulized Escherichia coli LPS (3 mg/ml; 15 min) 24 hours before determining bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) (A, D) and blood (C, F) neutrophil levels by cell counter. BAL protein content (B, E) was determined by Bradford assay. n = 8 (diet-induced) or 12 (db/db) mice per condition. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. ns = not significant.