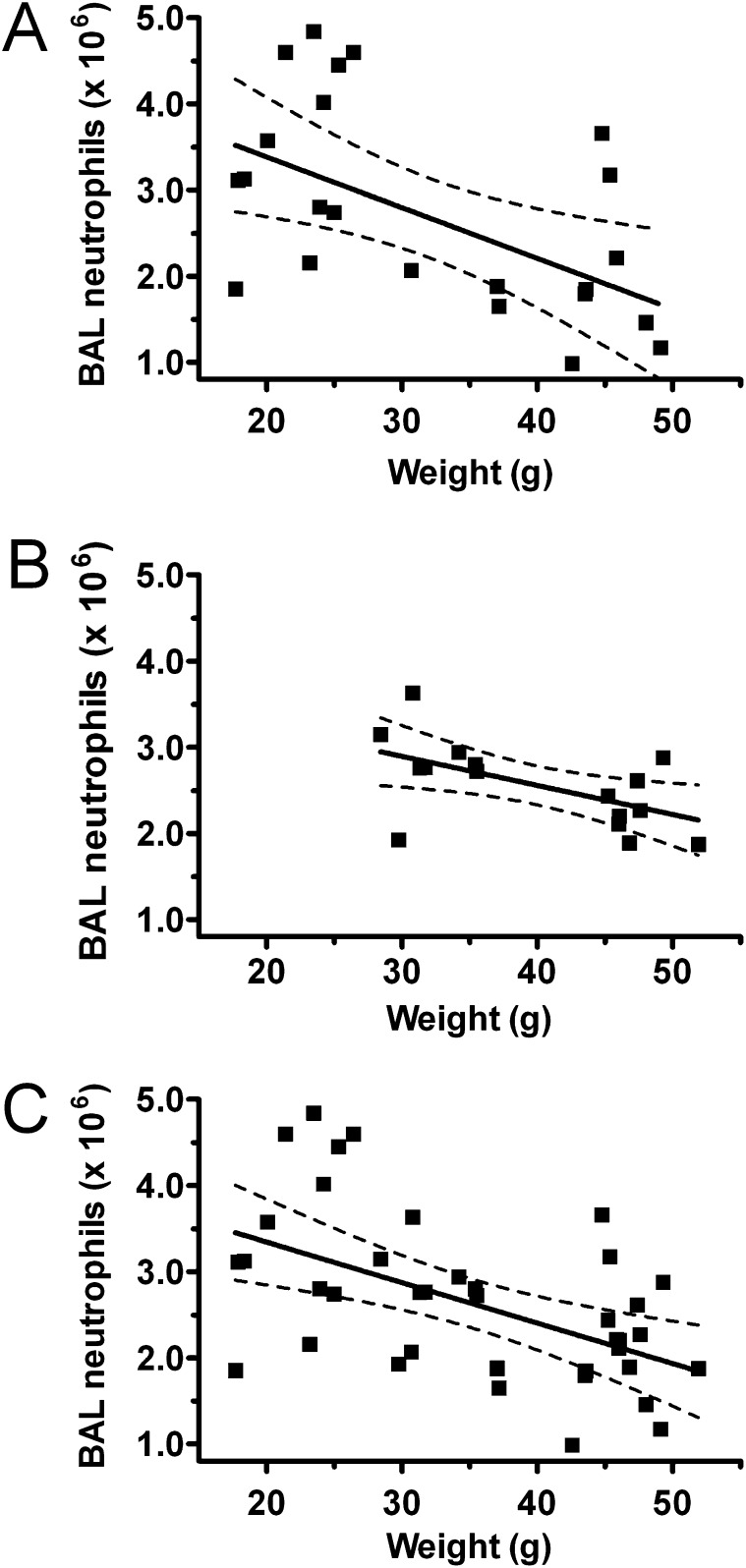
Figure 2.
Airspace neutrophilia is inversely related to mouse weight in LPS-injured lean and obese mice. BAL neutrophil levels 24 hours after nebulized LPS exposure in genetically obese (db/db) and lean (heterozygous littermate control) mice (A) and diet-induced obese (60% fat diet) and lean (10% fat diet) mice (B) were graphed versus mouse weights measured immediately before injury. Db/db mice: r2 = 0.27, P = 0.0096 by linear regression; diet-induced mice: r2 = 0.32, P = 0.02. Combining lean and obese mice from db/db and diet-induced models (C), an inverse relationship between weight and airspace neutrophilia remained and was not affected by mouse age or obesity model (P = 0.001, adjusted r2 = 0.25). Dashed lines indicate 95% confidence intervals.