Figure 4.
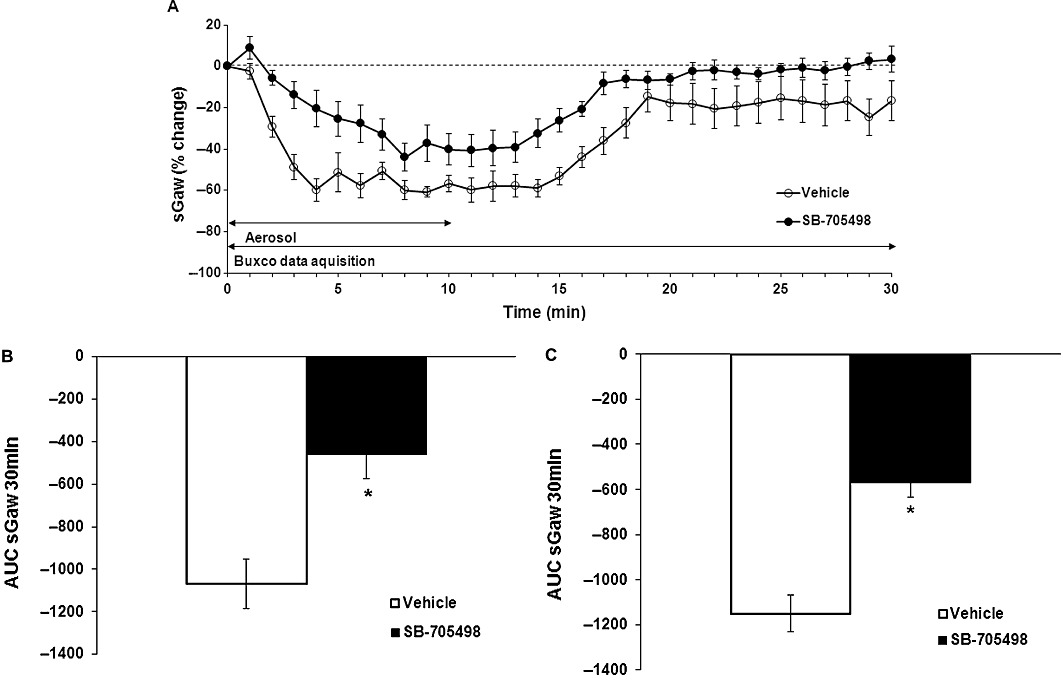
(A) Effect of SB-705498 10 mg·kg−1 p.o. (n = 11) on OA-evoked AHR to histamine (0.03 mg·mL−1) compared with methylcellulose 1 mL·kg−1 p.o. (n = 8) expressed as % change from the baseline sGaw values (10-min aerosol exposure then 20 min of recording) ± SEM. Negative values show a bronchoconstriction. (B) Effect of SB-705498 10 mg·kg−1 p.o. (n = 11) on OA-evoked AHR to histamine (0.03 mg·mL−1) (sGaw AUC for 30 min = −462 ± 114) compared with methylcellulose 1 mL·kg−1 p.o. (n = 8) (sGaw AUC for 30 min −1070 ± 116). Animals were dosed 1 h before OA and 2.5 h before a subthreshold dose of histamine. Negative sGaw AUC ± SEM values show a bronchoconstriction. *P < 0.05: significant inhibition of 57%. (C) Effect of SB-705498 10 mg·kg−1 p.o. (n = 9) on OA-evoked AHR to histamine (0.03 mg·mL−1) (sGaw AUC for 30 min = −569 ± 64) compared with methylcellulose 1 mL·kg−1 p.o. (n = 11) (sGaw AUC for 30 min −1151 ± 82). Animals were dosed after OA and 1 h before a subthreshold aerosol dose of histamine. Negative sGaw AUC ± SEM values show a bronchoconstriction. *P < 0.05: significant inhibition of 50%.
