Figure 10.
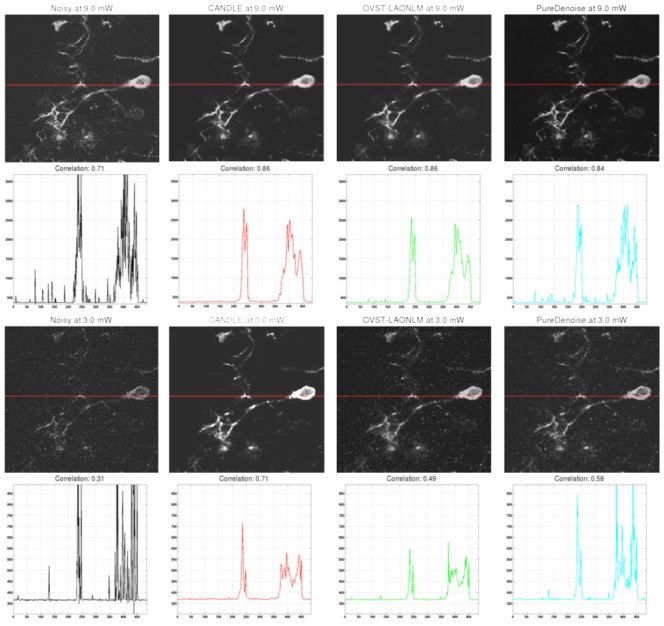
Denoising results obtained by the CANDLE, OVST-LAONLM and PureDenoise filters applied to the in vivo experiments on Xenopus laevis tectal neurons. Top (from left to right): noisy single image at highest power (9mW) and the corresponding denoised images obtained by the three methods compared. The correlation coefficient between each image and the mean reference image is provided just below. Second row: Intensity profiles for the horizontal line for the corresponding image in the first row. Third & fourth row: similar results obtained for images acquired at the lowest power (3mW). For denoised images, contrast was adjusted manually to minimize the appearance of residual spike noise to avoid saturation in the figure. For intensity profiles, identical axis range is used for all the methods and the noisy image. Saturation of the highest noise peaks was performed to display the signal of interest at an adapted scale.
