Figure 1.
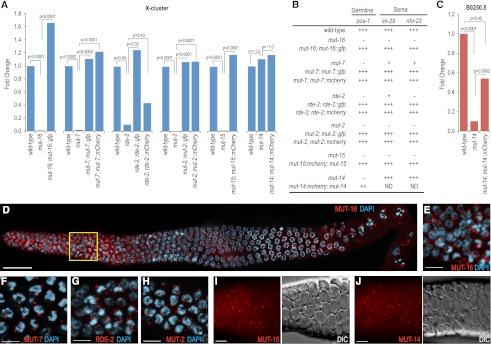
Mutator proteins localize to perinuclear foci in the germline. (A) Fluorescently tagged mutator proteins rescue mutations in their respective genes as assayed by TaqMan quantitative RT–PCR to detect the X-Cluster siRNA 22G siR-1. The mean is calculated from two biological replicates for each strain. (B) Susceptibility of mutator mutant worms to germline and somatic RNAi in the presence and absence of rescuing transgenes. pos-1 RNAi scored as complete embryonic lethality (that is, normal response to pos-1 RNAi) (+++), complete embryonic viability (that is, an RNAi-defective response) (−), or ∼50% embryonic viability (++). lin-29 RNAi scored as 100% vulval bursting (+++), 100% viable adults (−), or adults with morphological defects (i.e., protruding vulva) (+). nhr-23 RNAi scored as 100% larval arrest (+++), 100% viable adults (−), or adults with morphological defects (+). (C) mCherry-tagged MUT-14 rescues the mut-14(pk738) mutant as assayed by TaqMan quantitative RT–PCR of the germline-expressed B0250.8 siRNA. The mean is calculated from two biological replicates for each strain. (D) MUT-16 (red) localizes throughout the germline, but is brightest in the mitotic proliferation and transition zone regions as well as in the diplotene/diakinesis stages of meiosis. The yellow box is magnified in E. Image depicts entire dissected gonad stained with DAPI (blue) and anti-GFP (recognizing MUT-16::GFP). Image is an assembly of four three-dimensional (3D) data stacks following deconvolution. Bars, 20 μm. (E–J) Mutator proteins localize to foci in the germlines of adult hermaphrodites. MUT-16::GFP (E), MUT-7::GFP (F), RDE-2::GFP (G), and MUT-2::GFP (H) associate with the nuclear periphery as visualized by DAPI staining (blue). MUT-15::mCherry (I) and MUT-14::mCherry (J) mCherry fluorescence images are displayed next to the corresponding DIC images. All animals were dissected prior to imaging. Bars, 5 μm.