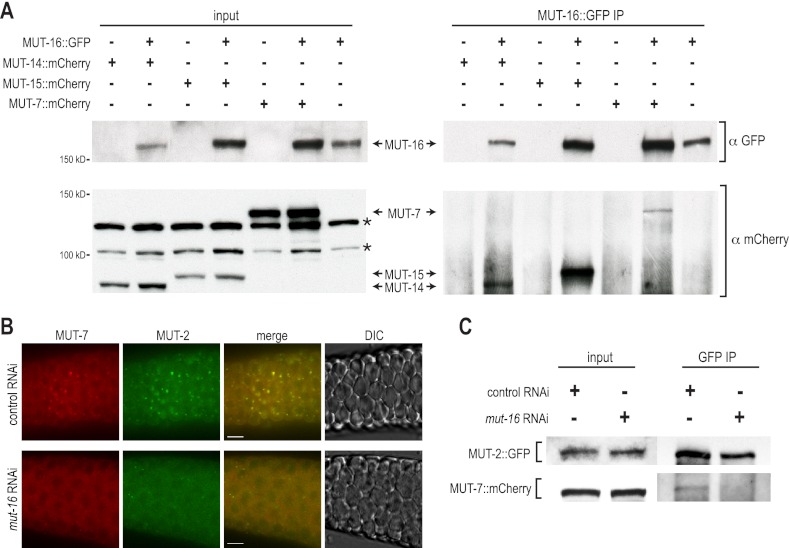
Figure 5.
MUT-16 is essential for mutator complex formation. (A) GFP and mCherry proteins from total lysate (input, left panels) and GFP-IP (right panels) from the indicated transgenic strains as assayed by Western blot. MUT-14::mCherry (93.1 kDa), MUT-15::mCherry (96.1 kDa), and MUT-7::mCherry (139.5 kDa) coimmunoprecipitate with MUT-16::GFP (154.4 kDa). Asterisks mark bands resulting from cross-reactivity of anti-mCherry with non-mutator proteins. (B) MUT-7::mCherry (red) and MUT-2::GFP (green) expression in C. elegans treated with control or mut-16 RNAi. (C) GFP and mCherry proteins from total lysate (input, left panels) and GFP-IP (right panels) from the transgenic strain containing MUT-2::GFP (86.6 kDa) and MUT-7::mCherry (139.5 kDa) treated with control or mut-16 RNAi and assayed by Western blot.