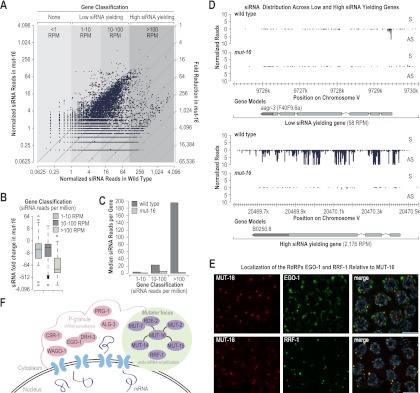
Figure 6.
MUT-16 is required for siRNA amplification. (A) Scatter plots display small RNA RPM on a log2 scale for each annotated coding gene in wild-type (bottom axis) and mut-16 mutants (left axis). The fold reduction of siRNA reads in mut-16 mutants relative to wild type is indicated by the diagonal lines on the right axis. (B) Box plots display ratio of siRNA reads on a log2 scale in mut-16 relative to wild type for low siRNA yielding genes (1–10 RPM or 10–100 RPM) and high siRNA yielding genes (>100 RPM). (C) Median siRNA reads per gene for low siRNA yielding genes (1–10 RPM or 10–100 RPM) or high siRNA yielding genes (>100 RPM) in wild-type and mut-16 mutants. (D) Small RNA distribution across the low siRNA yielding gene aagr-3 and the high siRNA yielding gene B0250.8 in wild-type and mut-16 mutants. (E) Localization of HA::EGO-1 and Flag::RRF-1 relative to MUT-16::GFP in dissected germlines immunostained with anti-GFP and either anti-HA or anti-Flag antibodies. Bars, 5 μm. (F) Model depicting the composition and localization of Mutator foci and P granules adjacent to nuclear pores.