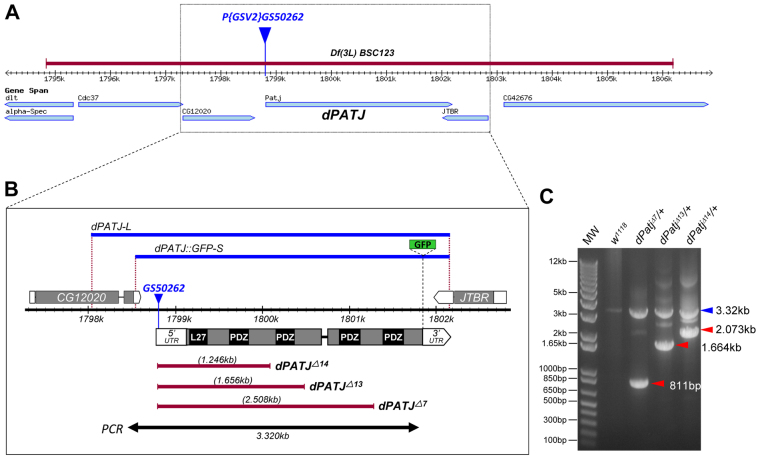
Fig. 1.
Characterization of dPatj null mutants generated by imprecise P-element excision. (A) The Drosophila Patj (dPatj) locus. GS50262 (blue triangle) is inserted at 1,798,845 bp of the third chromosome (http://flybase.org/reports/FBti0109626.html). The Df(3L)BSC123 deletion is indicated (red bar). (B) Deletions in dPatjΔ7, dPatjΔ13 and dPajΔ14 (red bars), the region covered by the PCR in C (black bar), and the genomic fragments used in VK20-dPatj-L and VK20-dPatj::GFP-S (blue bars) are shown. dPatj-L starts in the middle of the CG12020 coding sequence, whereas dPatj::GFP-S starts immediately after the CG12020 stop codon; both end in the 3′UTR of JTBR. In dPatj::GFP-S, GFP is inserted in frame before the dPatj stop codon. (C) PCR verification of dPatjΔ7, dPatjΔ13 and dPajΔ14 mutants. PCR products are indicated for the wild-type (w1118) chromosome (3.32 kb, blue arrowhead) versus the dPatjΔ7, dPatjΔ13 and dPajΔ14 mutant chromosomes (red arrowheads). MW, DNA ladder.