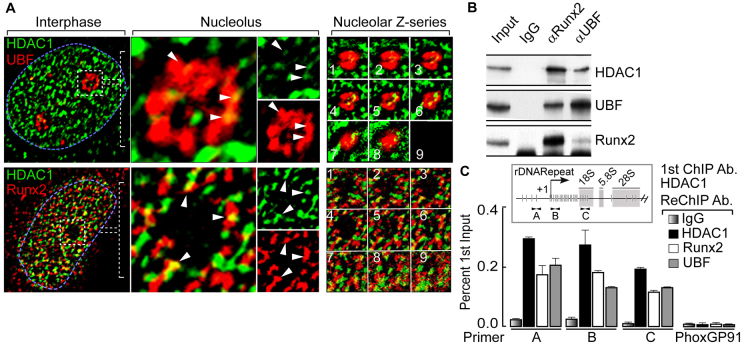
Fig. 1.
HDAC1 colocalizes with RUNX2 and UBF in the interphase nucleolus. (A) Immunofluorescence microscopy in SaOS-2 cells demonstrates HDAC1 colocalization with UBF (upper panels) and RUNX2 (lower panels) at the nucleolar periphery. The blue dotted line represents the nucleus and the white dotted box marks a nucleolus. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation assays show that HDAC1 associates with UBF and RUNX2 in proliferating osteosarcoma cells. (C) ChIP-ReChIP experiments show the binding of HDAC1 together with RUNX2 and UBF at rDNA repeats (primer A, B and C). Primary (1st) ChIP was performed using anti-HDAC1 antibody (Ab) followed by ReChIP (2nd) using anti-HDAC1, anti-RUNX2 and anti-UBF antibodies. A Phox-GP91 gene primer was used as a negative control to demonstrate the specificity of the ChIP-ReChIP assays. In the inset, a single rDNA repeat is shown with the location of the primer sets used in ChIP assays (A, B and C) at different regions of the rDNA. Vertical lines indicate the RUNX2-binding sites at the rDNA repeat. White arrows show the location of primers.