Fig. 5.
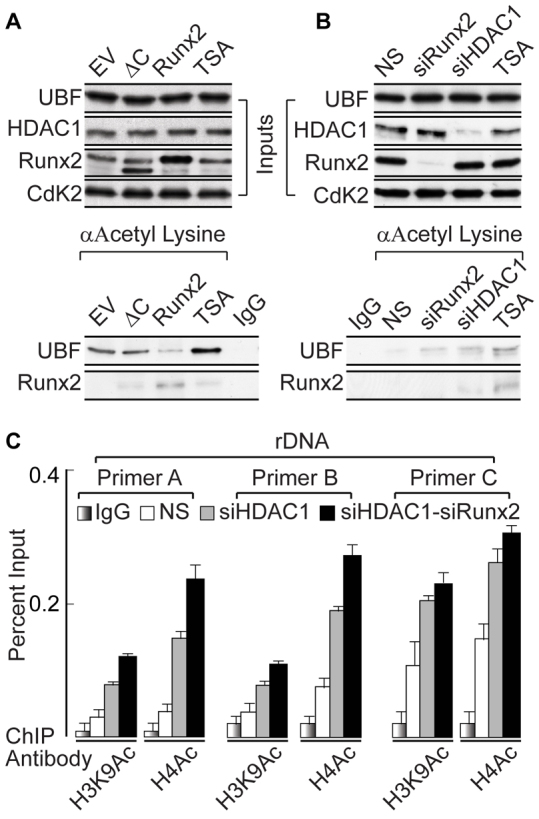
Deacetylation of UBF requires RUNX2-mediated HDAC1 recruitment. (A) Western blots showing the effect of expression of wild-type RUNX2 and the ΔC mutant after 48 hours of lentiviral infection in SaOS-2 cells. Samples were also treated with the histone deacetylase inhibitor TSA as control (upper panel). An immunoprecipitation assay was performed using an antibody against acetylated lysine, demonstrating decreased UBF acetylation in the presence of wild-type RUNX2 but not the ΔC mutant when compared with empty vector (EV) controls (lower panel). (B) Western blots demonstrating the depletion of RUNX2 and HDAC1 by siRNA oligonucleotides and treatment with TSA (upper panel). An antibody against acetylated lysine was used for immunoprecipitation. There is an increase in UBF acetylation in siRUNX2, siHDAC1 and TSA-treated samples, when compared with the non-silencing (NS) control (lower panel). (C) ChIP analysis showing that there is an increase in active histone marks (H3K9Ac and H4Ac) associated with rDNA, in the absence of HDAC1 alone or upon combined depletion of HDAC1 and RUNX2 after 48 hours of siRNA oligonucleotide treatment, as assessed by use of rDNA primer A, B and C.
