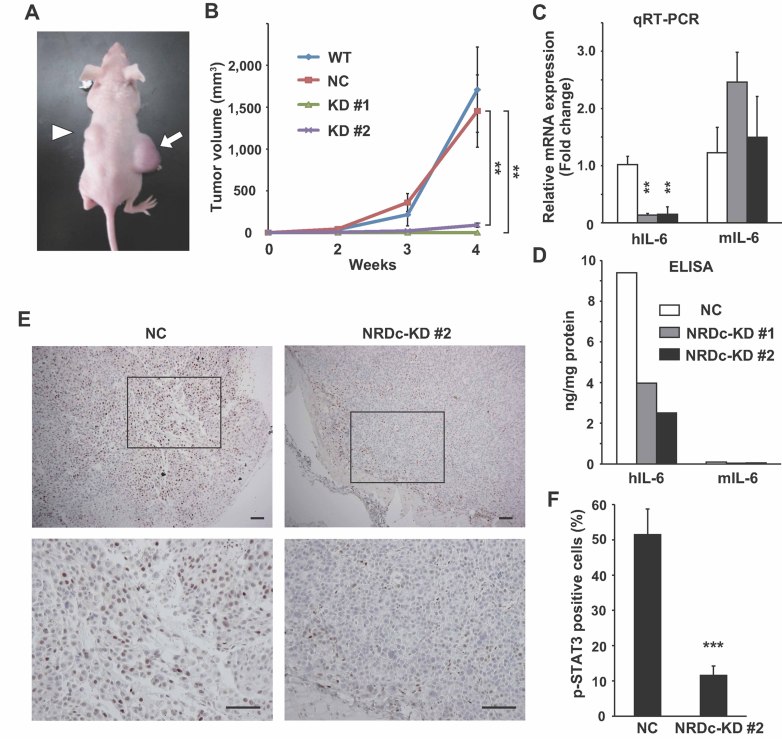
Figure 7. NRDc is essential for tumour growth of xenotransplanted gastric cancer cells.
- The WT or each stable TMK-1 cells were injected subcutaneously into the flanks of nude mice. The photograph shows the representative tumours grown from the NC (arrow) and NRDc-KD #2 cells (arrowhead) at 4 weeks after inoculation.
- Tumour volume of each xenograft calculated at the indicated time points is plotted. Combined results of two-independent experiments are shown as mean ± SEM with total n = 8 per each clone.
- qRT-PCR was performed using RNA extracted from tumours at 4 weeks after xenotransplantation. Data represent mean ± SEM of three-independent tumours of each clone.
- Human or mouse IL-6 protein concentration in the indicated tumours was quantified using species-specific ELISA kits.
- Tumour tissues at 4 weeks after xenografting were processed for immunohistochemical analysis with anti-phspho-STAT3 antibody. Representative microphotographs of tumours from the NC (left panels) or KD #2 TMK-1 cells (right panels) are shown. Lower panels are magnified photographs of the boxed areas. Scale bar, 100 µm.
- Ratios of the tumour cells expressing p-STAT3 in the peripheral regions of the grown tumours are shown. Values represent mean ± SD from randomly selected tumour fields (n = 10).