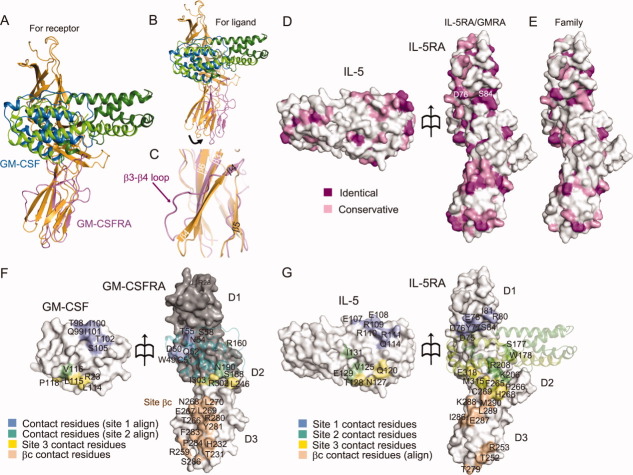
Figure 4.
Structural comparison and surface properties of the binding interface between IL-5•IL-5RA and GM-CSF•GM-CSFRA. Superimposition of GM-CSFRA (light purple) bound to GM-CSF (blue) for the IL-5RA D3 domain (A) and for the IL-5 chain B (B), shown as a ribbon diagram. (C) Close-up view of the superimposition in (A) between the IL-5RA and the GM-CSFRA D3 domains. (D) Residue conservation mapping on the surfaces of IL-5 and IL-5RA. Purple and pink surfaces indicate the locations of identical and similar residues between IL-5•IL-5RA and GM-CSF•GM-CSFRA, respectively, among receptor α of the human βc family (E), according to the sequence alignment in Supporting Information Fig. S1A. (F) Contact residue mapping on the surfaces of GM-CSF and GM-CSFRA. The D1 and D2 domains of GM-CSFRA were modeled based on the structure of IL-5RA by MODELLER, and are colored gray. Blue and green surfaces indicate the locations of putative contact residues with GM-CSF•GM-CSFRA, based on the sequence alignment, the contact residues with sites 1 and 2, and yellow and wheat surfaces indicate the contact residues with site 3 and βc, respectively. (G) Contact residue mapping on the surfaces of IL-5 and IL-5RA. Blue, green, yellow, and wheat surfaces indicate the locations of contact residues with sites 1, 2, and 3, and putative contact residues with βc, respectively, based on the sequence alignment.