Figure 1.
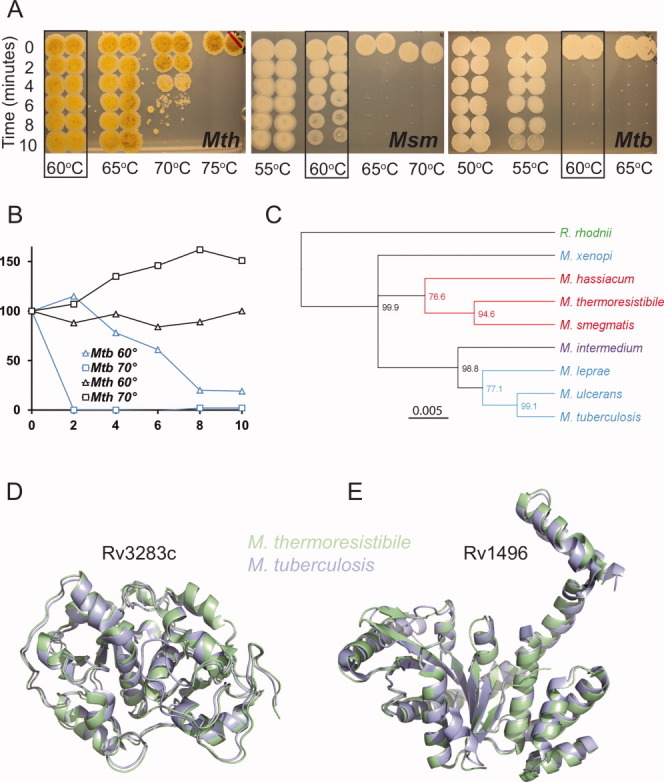
Mth is more heat-resistant than Mtb and Mth and Mtb structures are highly similar. A: Mth survives heating to 70°C for short periods, as shown by cfu assay. Mtb begins to lose viability at 55°C and is killed at 60°C. Msm shows intermediate heat resistance. Boxes indicate survival at 60°C. Mth shows characteristic yellow pigmentation. B: Metabolic activity as measured by alamarBlue assay shows disappearance of reducing potential in Mtb after 10 min heat shock at 60°C, whereas Mth is not affected even at 70°C. One representative of at least three independent experiments is shown. C: Phylogenetic tree of eight Mycobacterium 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) sequences. Sequences were aligned with the outgroup sequence from shared suborder Rhodococcus rhodnii. The unrooted HKY UPGMA tree is based on 1475 aligned nucleotide positions of the 16S rRNA gene, and bootstrap consensus percentages over 50% are shown at the nodes. Branch color represents growth rate, where blue is slow, red is rapid, purple is intermediate. Green denotes non-mycobacterial. D: Superposition of the sulfurtransferase SseA (Rv3283) and E: RAS superfamily GTPase (Rv1496) with their Mth orthologs shows almost identical folds.
