Figure 5.
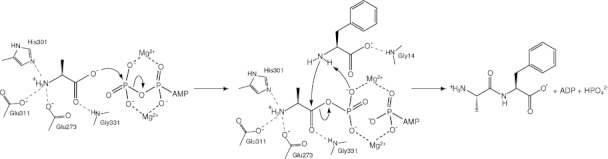
Schematic drawing of the reaction mechanism for the dipeptide synthesis catalyzed by BacD. The residues involved in the interaction with the dipeptide moiety of the P-analog are shown. The first step is the formation of the acylphosphate intermediate where the carboxy oxygen atom in l-alanine is nucleophile. The second step includes the formation of the tetrahedral intermediate and the release of the phosphate group, where the carbonyl carbon is electrophile and the phosphate group deprives the amido nitrogen atom of a proton.
