Figure 5.
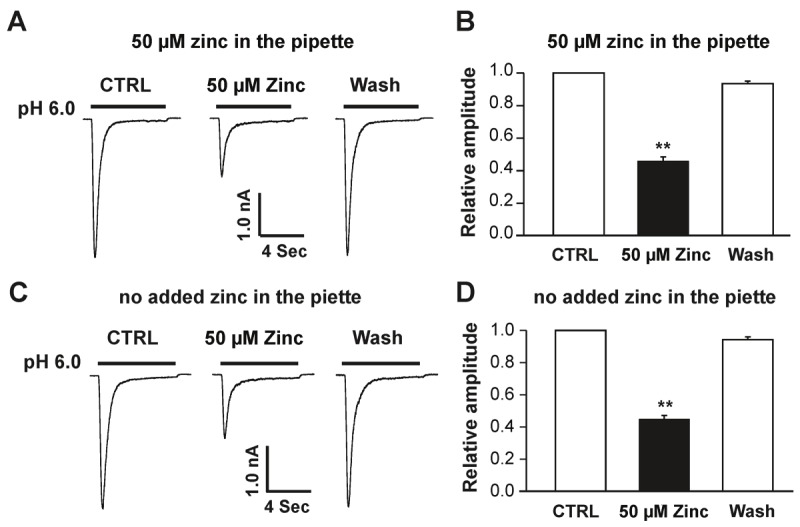
Extracellular zinc is responsible for inhibition of the hASIC1b current in hASIC1b transfected CHO cells. A, Representative traces showing that inhibition of hASIC1b currents by bath application of 50 μM zinc (extracellular zinc) was not affected by inclusion of 50 μM zinc in the pipette solution (i.e. intracellular zinc). hASIC1b currents were activated by a drop in pH from 7.4 to 6.0. B, Quantification of relative peak amplitude of zinc inhibition in the presence of 30 μM zinc in the pipette. Each point represents the average response of six cells. C, Original traces showing that inhibition of hASIC1b currents by bath application of 50 μM zinc (extracellular zinc) under no added zinc in the pipette. hASIC1b currents were triggered by a drop in pH from 7.4 to 6.0. D, Quantification of relative peak amplitude of zinc inhibition under no added zinc in the pipette. Each point represents the average response of five cells. Asterisk indicates values significantly different from the control, t-test, **p < 0.01. CTRL represents control.
