Figure 6.
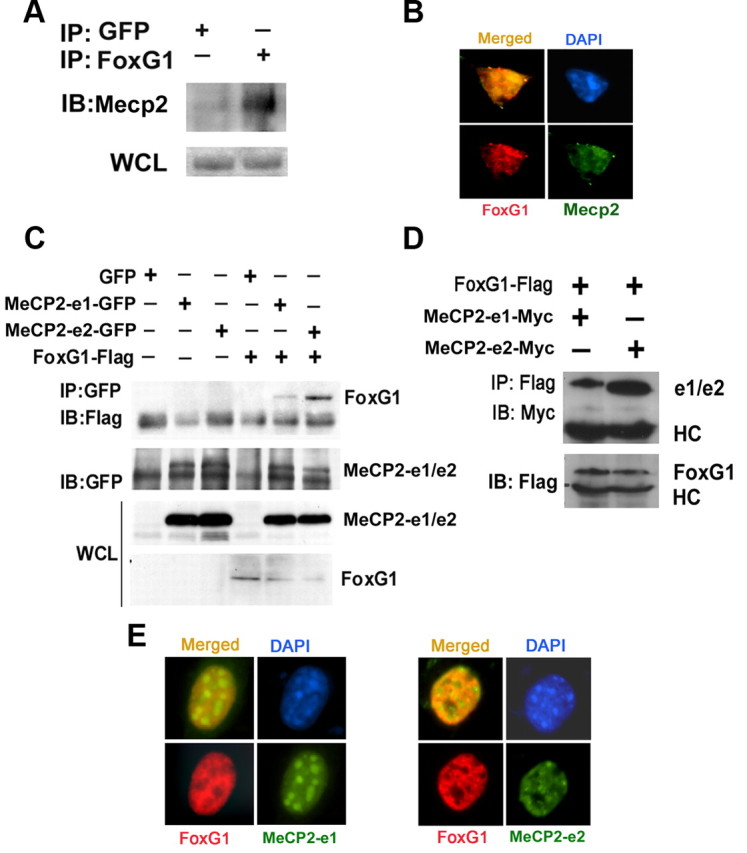
Analysis of interaction between FoxG1 and Mecp2. A, CGN lysates were subjected to coimmunoprecipitation using FoxG1 antibody. The immunoprecipitate was analyzed by Western blot using MeCP2 antibody. FoxG1 was able to pull down Mecp2; however, GFP was unable to pull down Mecp2. An aliquot of the WCL (whole cell lysate) was also analyzed for Mecp2. B, Immunocytochemical analysis of CGNs using antibodies against FoxG1 and Mecp2. Mecp2 and FoxG1 colocalize. C, Lysates from HEK293T cells transfected with GFP, MeCP2–e1-GFP, MeCP2–e2-GFP, and Flag-FoxG1 plasmids as shown were immunoprecipitated using GFP antibody. Immunoblotting (IB) was performed using Flag antibody (top) and then reprobed with GFP antibody (bottom). Western blotting of WCL using GFP and Flag antibodies is also shown. FoxG1 interacts with both the isoforms of MeCP2 with a greater affinity for MeCP2–e2 isoform IP indicates immunoprecipitation. D, Lysates from HEK293T cells cotransfected with FoxG1-Flag and MeCP2–e1-Myc or MeCP2–e2-Myc were immunoprecipitated using Flag antibody. The immunoprecipitate was subjected to immunoblotting with Myc antibody (top). The blot was reprobed with Flag antibody (bottom). FoxG1 interacted with MeCP2–e2 isoform more strongly than the MeCP2–e1 isoform. E, HT22 cells were cotransfected with FoxG1-Flag and either MeCP2–e1-GFP or MeCP2–e2-GFP followed by immunocytochemistry using Flag and GFP antibodies. MeCP2–e2 and FoxG1 colocalize more than MeCP2–e1 and FoxG1.
