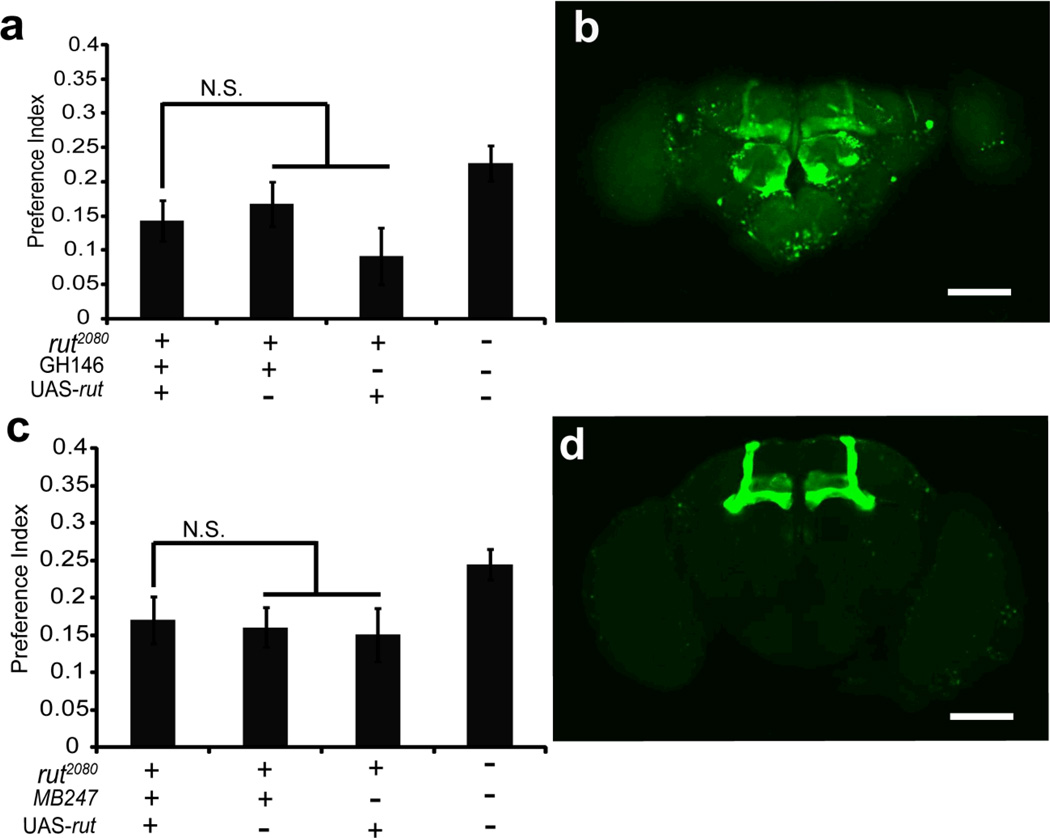
Figure 3. The ethanol preference phenotype of rut2080 mutants is separable from simple appetitive olfactory learning.
Both GH146 and MB247 rescue the olfactory appetitive learning defect in rut2080. However, they cannot rescue ethanol preference defect in rut2080. (a) The expression of rut driven by the projection neuron driver GH146-Gal4 failed to rescue the rut2080 ethanol preference phenotype, since the ethanol preference of the genotype rut2080; GH146/+; UAS-rut/+ was not significantly difference from both negative controls. (b) GH146-Gal4 drives GFP expression in antennal lobe, olfactory projection neurons and partial mushroom body. (c) Likewise, the expression of rut driven by the MB247-Mushroom body Gal4 line also failed to rescue the rut2080 ethanol preference phenotype, since the preference index of the genotype rut2080;;UAS-rut/MB247 was not significantly difference from both negative controls. (d) MB247-Gal4 drives GFP expression in α/β and γ lobe. Data are mean ± S.E.M. “N.S.” means no significance.