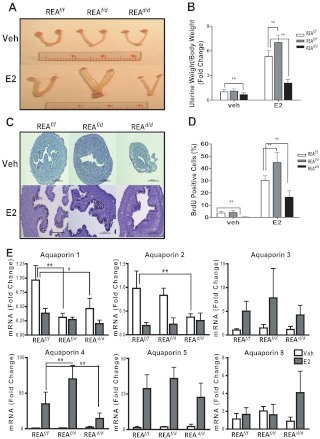
Fig. 1.
Uterine growth and cell proliferation in response to E2 are enhanced in REAf/d (heterozygous) mice and reduced in REAd/d (homozygous) mice and are accompanied by changes in the expression of AQP genes. A, Uteri from vehicle or E2-treated REAf/f, REAf/d, and REAd/d mice. Mice, 21 d of age, were injected once daily with control vehicle or E2 for 4 d, and uteri were harvested 24 h after the last injection. B, Uterine weight gain in response to E2 was monitored and normalized to each animal's body weight. C, BrdU immunohistochemistry in uteri from REAf/f, REAf/d, and REAd/d mice treated with vehicle (Veh) or E2 for 4 d and injected ip with BrdU at 2 h before harvesting of uteri (magnification, ×20). Scale bar, 200 μm. D, Percentage of BrdU-positive epithelial cells/total cells monitored in at least six ×40 fields. E, mRNA levels of AQP known to be expressed in the mouse uterus were monitored by qRT-PCR in mice at age 21 d treated with control vehicle or E2 for 4 d. Uteri were harvested and RNA isolated at 24 h after the last injection of E2 or vehicle. The data are mean ± sd (n = 10 per group), and mRNA levels are illustrated as relative expression normalized to 36B4 by vehicle-treated wild type. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.