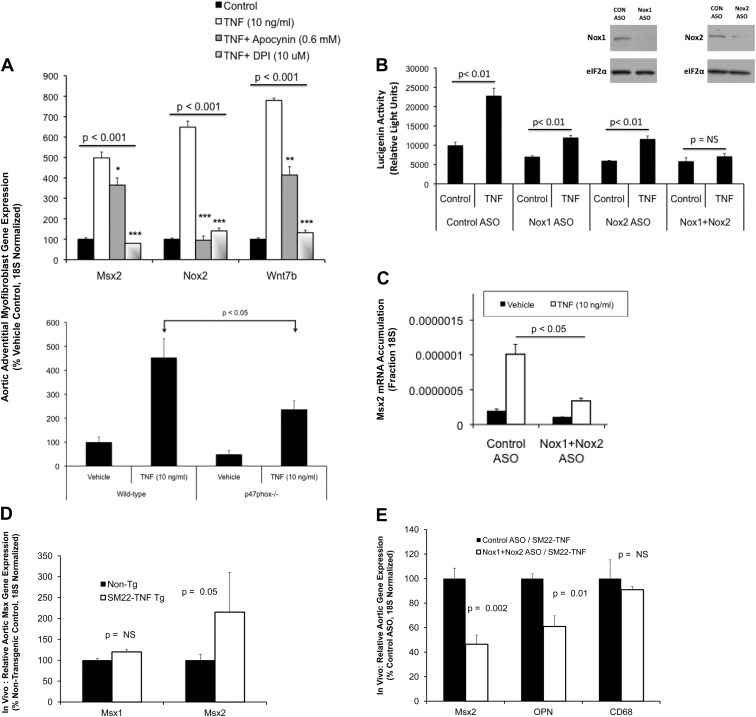
Fig. 2.
TNF induction of Msx2 gene expression requires intact Nox and mitochondrial redox signaling. A, Treatment of primary aortic myofibroblasts with the Nox inhibitor apocynin partially reduced Msx2 while completely preventing TNF induction of Nox2. DPI, a dual inhibitor of Nox and mitochondrial respiration, abrogated TNF induction of both Msx2 and Nox2 (n = 3 per group; replicated > 10 times). Wnt7b responses parallel those of Msx2. Lower panel, Myofibroblasts from mice deficient for p47phox−/−, an obligatory coregulator of Nox1 and Nox2 activity and target of apocynin inhibition, exhibit significantly reduced Msx2 induction (n = 3 per treatment; P < 0.05). ASO directed toward Nox1 and Nox2 reduced TNF-induced oxidative stress (B) and Msx2 induction (C; n = 4 / group; replicated more than three times). Nox1 and Nox2 ASO concentrations were each at 0.25 μm and the control ASO (CON ASO) at 0.5 μm. B, inset, Western blot analyses confirm reductions in Nox1 and Nox2 protein levels with ASO treatment. Pharmacological inhibitors were introduced 30 min before treatment with TNF, and cultures were incubated overnight with the indicated ASO before TNF treatment. D, Mice transgenic for SM22-TNF express elevated aortic Msx2 but not Msx1 (n = 6–8 per genotype; P = 0.05). E, As in vitro, administration of Nox1+Nox2 ASO (n = 8) significantly reduces aortic Msx2 in vivo in SM22-TNF transgenic mice vs. control ASO (n = 6). OPN, another TNF target, is also reduced, whereas macrophage CD68 is not. *, P < 0.05 vs. TNF; **, P < 0.01 vs. TNF; ***, P < 0.001 vs.TNF.