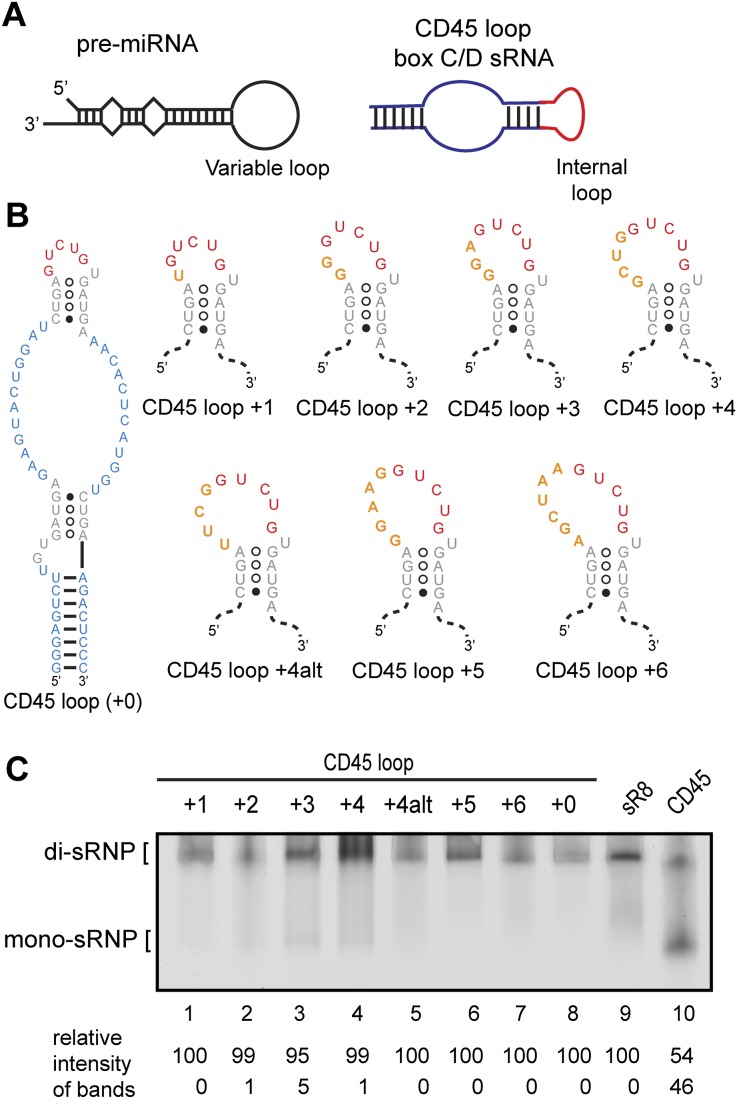
FIGURE 3.
sRNAs with a wide variety of internal loops confer di-sRNP assembly. (A) Hairpin stem–loops are a prevalent secondary structure in at least two classes of small noncoding RNAs: pre-microRNAs (pre-miRNAs) and box C/D s(no)RNAs. The exact number and location of base pairs vary within each class of RNAs—these diagrams are not to scale. (B) Secondary structures of CD45 loop mutants. The internal loop from the CD45 loop sRNA was mutated to include additional nucleotides of the randomized sequence. Box C/D and C′/D′ sequences (gray); sequences originating from CD45 (blue); sequences originating from sR8 (red); randomized sequences inserted in the internal loop (orange). The size of each loop in relation to the 5-nt loop of CD45 is indicated (+1, +2, etc.). (C) Assembly of Ss sRNPs with sRNAs bearing a wide variety of internal loops. Each sRNA mutant was in vitro–transcribed and assembled with Ss box C/D core proteins and assayed for di-sRNP formation by native gel electrophoresis. sRNPs assembled with sR8 and CD45 sRNAs are included as markers for di- and mono-sRNP formation. Quantitations of the relative intensity of di- and mono-sRNP sized bands are indicated.