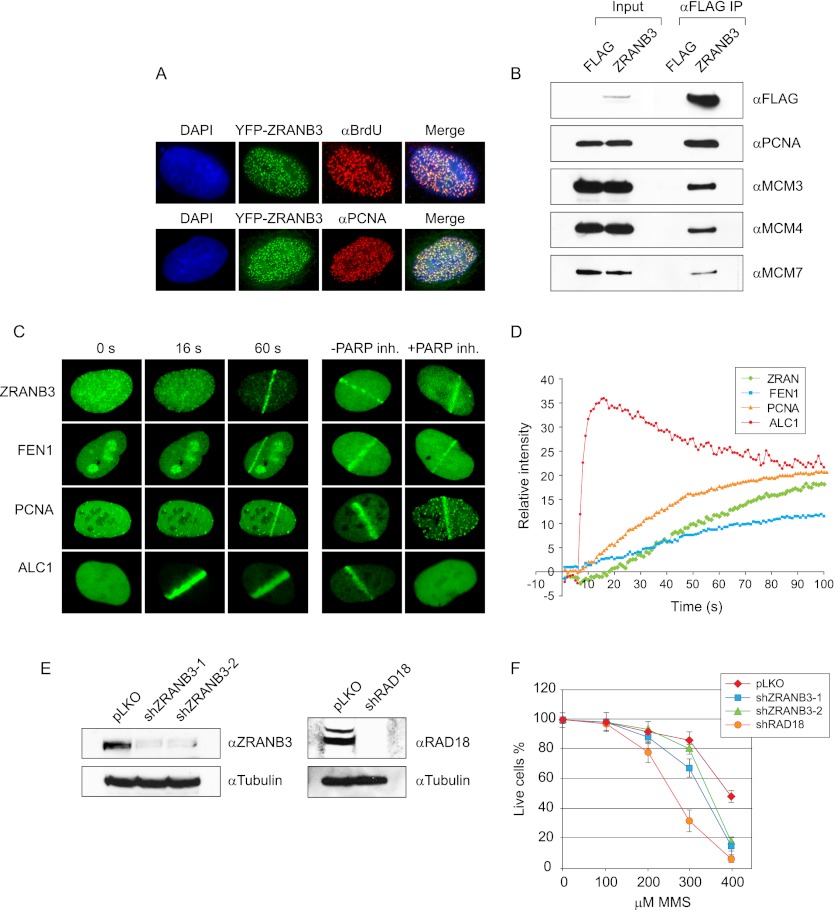
Figure 1.
(A) ZRANB3 targets sites of DNA replication. U2OS cells were transiently transfected with YFP-ZRANB3, pulsed with BrdU for 15 min, and stained with anti-BrdU antibody. Alternatively, cells were transfected with YFP-ZRANB3 and stained against endogenous PCNA. (B) Interaction of ZRANB3 with replication-associated factors. 293T cells were transiently transfected with Flag-tagged ZRANB3 or with empty vector, and extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation on anti-Flag beads. Immunocomplexes were eluted with 3xFlag peptide and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (C) ZRANB3 is recruited to the sites of laser-induced DNA damage. U2OS cells were transiently transfected with the indicated YFP constructs and analyzed by live-cell imaging. Shown are representative images at the indicated time points post-damage. Recruitment of ZRANB3 is compared with the replication factors PCNA and FEN1 and the SNF2 chromatin remodeling factor ALC1. Cells were also assayed 60 sec after the damage in the presence or absence of a PARP inhibitor. (D) Kinetics of the ZRANB3 recruitment to sites of laser-induced DNA damage, and comparison with the kinetics of PCNA, FEN1 and ALC1. More than 10 cells were analyzed for each construct. (E) Down-regulation of ZRANB3 and RAD18 expression by shRNA. Stable cell lines were created by the expression of empty pLKO-Puro, shZRANB3-1, shZRANB3-2, and shRAD18 vectors. Following selection against puromycin, the expression of ZRANB3 or RAD18 was evaluated by Western blotting. (F) Sensitivity of ZRANB3-deficient cells to MMS.