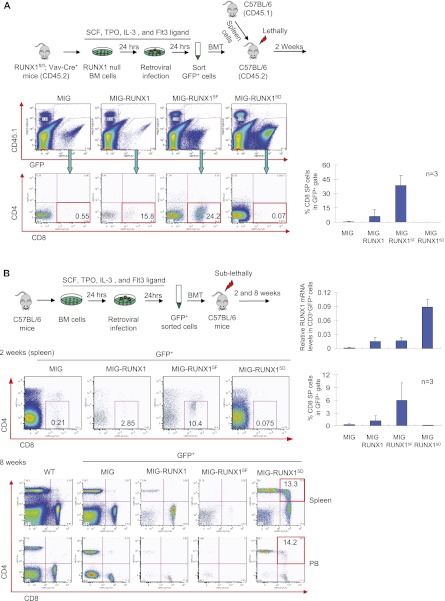
Figure 5.
Inhibitory role of tyrosine phosphorylation on RUNX1 function in CD8 T-cell differentiation. (A) Rescue assay of CD8 T-cell differentiation. (Top) Schematic diagram of retroviral transduction rescue experiments of bone marrow from Runx1fl/fl, Vav-Cre mice. (Bottom left) Representative flow cytometric plots for GFP, CD45.1, CD4, and CD8 of spleen cells from recipient mice 2 wk following transplantation. (Right) Quantitation of flow cytometry data (n = 3; error bars represent mean ± SEM). (B) Dominant effects of RUNX1 tyrosine phosphorylation mutants on T-cell differentiation. (Top left) Schematic diagram of retroviral transduction experiments of bone marrow from wild-type C57BL/6 mice. (Bottom) Representative flow cytometry plots for CD4 and CD8 of GFP+ cells from spleen or peripheral blood (PB) at 2 or 8 wk following transplantation. (Top right) qRT–PCR analysis for RUNX1 mRNA levels from CD3+GFP+-sorted splenocytes at 2 wk. (Bottom right) Quantitation of the flow cytometry data at 2 wk (n = 3; mean ± SEM).