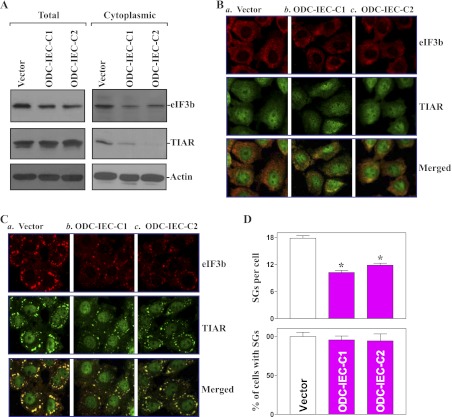
Fig. 1.
Increasing the cellular polyamines by ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) overexpression represses the assembly of stress granules (SGs). A: levels of total and cytoplasmic eukaryotic initiation factor 3b (eIF3b) and T-cell intracellular antigen-1 (TIA-1)-related protein (TIAR) proteins in stable ODC-intestinal epithelial cells (ODC-IECs). IEC-6 cells were infected with either the retroviral vector containing the sequence encoding mouse ODC cDNA or control retroviral vector. The clones resistant to the selection medium were isolated and screened for ODC expression. Whole cell lysates and cytoplasmic proteins were prepared for Western immunoblotting analysis. Twenty micrograms of total or cytoplasmic proteins were applied to each lane, and immunoblots were hybridized with the antibody specific for eIF3b or TIAR. After the blot was stripped, actin immunoblotting was performed as an internal control for equal loading. B: cellular distribution of eIF3b and TIAR as measured by immunofluorescence staining assays in stable ODC-IECs: cells infected with control vector (a) and clones (C) of cells infected with ODC expression vector (b and c). Cells were permeabilized and incubated with the anti-eIF3b or -TIAR antibody and then with anti-IgG conjugated with Alexa Fluor. eIF3b was shown as red, whereas TIAR was shown as green. Original magnification, ×250. C: changes in arsenite-induced assembly of SGs in cells described in B. After stable ODC-IECs were treated with 0.5 mM arsenite for 45 min, the formation of SGs was examined by staining eIF3b and TIAR. D: quantification of the percentage of cells containing stress granules (bottom) and the numbers of stress granules per cell (top) in cells described in C. Values are means ± SE of data from 6 samples. *P < 0.05 compared with the vector alone.