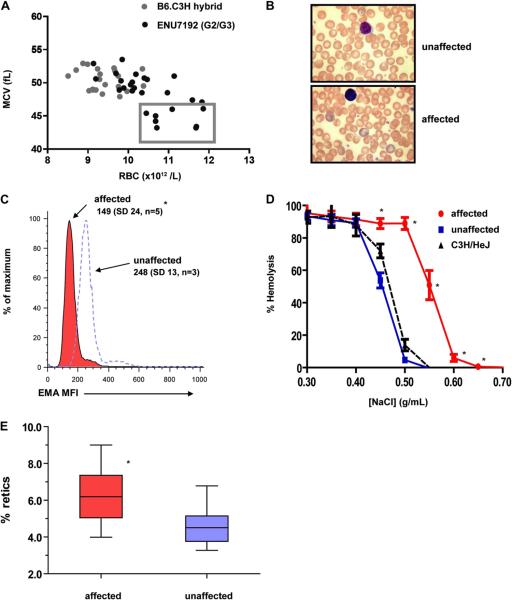
Figure 1.
The RBC phenotype of an ENU-generated mutant mouse strain ENU7192 demonstrates diagnostic features of human hereditary spherocytosis. (A) Enumeration and MCV of RBC parameters of individual mice from a B6.C3H control hybrid strain (gray) and generation 2 and 3 (G2/3) progeny of mutagenized strain ENU7192 (black). Individual affected mice with RBC count and MCV parameters deviating by more than 2 SDs (box) from nonaffected littermates and nonmutagenized hybrid controls were selected for heritability testing and mapping. (B) Wright-Geimsa stain of PB smear of unaffected (upper panel) and affected (lower panel) ENU7192 at 400× magnification. (C) Histogram of mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of RBCs labeled with eosin-5′-maleimide (EMA) where affected (red) and nonaffected (open peak) mice are defined by the low MCV parameter and confirmed by prospective PCR genotyping for the E924X or WT Ank1 genotypes (see Supplementary Figure E1; online only, available at www.exphem.org). The mean MFI values and SDs are shown. (D) Osmotic hemolysis plot of RBCs from affected (● red) and nonaffected (■ blue) ENU7192 (C3H N8–9) mice and C3H/HeJ parental strain (▲ black, dashed lined) (n = 4–7 mice per strain). (E) Affected mice (red) have increased percent of circulating reticulocytes compared to nonaffected littermates (blue). *Significantly different than unaffected mice with p < 0.05.