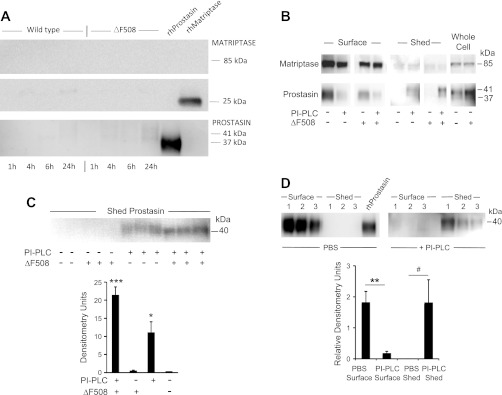
Fig. 6.
Spontaneous and induced shedding of matriptase and prostasin from CFBE41o− bronchial epithelial cells. A: results of immunoblotting to detect spontaneous shedding into apical medium by polarized monolayers of ΔF508 CFTR-homozygous (“ΔF508”) CFBE41o− cells or the same line of cells complemented with wild-type CFTR (“Wild type”). Cells were incubated with medium bathing apical and the basolateral surfaces to mimic conditions under which apical protease activity was assayed in living cells (see Fig. 4). Medium harvested at the intervals noted was electrophoresed and immunoblotted using protease-selective antibodies. Immunoblots in B explore apical expression and modes of membrane attachment by proteases in cells cultured under liquid conditions. ΔF508 and wild-type CFBE41o− cells were incubated with PBS or with phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) to release glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored proteins. Apical protease expression with or without exposure to PI-PLC was detected in purified preparations of apically biotinylated surface proteins and compared with expression in unbiotinylated whole cell extracts. The immunoblot in C reveals PI-PLC-induced shedding of prostasin in unbiotinylated ΔF508 and wild-type cells cultured for 10 days at an air interface followed by 1-h exposure to PI-PLC in liquid medium. The graph compares prostasin band density in ΔF508 and wild-type cells with and without exposure to PI-PLC. *P < 0.05, PI-PLC-exposed ΔF508 vs. wild-type; ***P < 0.001, PI-PLC-exposed vs. unexposed ΔF508 cells. D: comparison of apical surface prostasin to prostasin shed into medium by wild-type cells in liquid culture exposed apically to PBS or PI-PLC. Band density is normalized to density of recombinant prostasin band (equal amounts loaded for each gel). **P = 0.01, apical surface prostasin in PBS- vs. PI-PLC-exposed cells; #P = 0.07, shed prostasin in PBS- vs. PI-PLC-exposed cells.