Fig. 2.
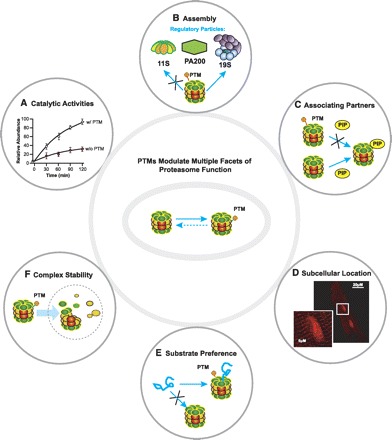
PTMs of proteasomes modulate several facets of proteasome function. PTMs act as a mechanism by which proteasomes can achieve instantaneous and/or chronic regulation to respond to a dynamic cellular environment. The following functions of proteasomes are known to be regulated by PTMs: caspase-like, trypsin-like, and chymotrypsin-like catalytic activities (A), assembly of 20S with regulatory particles (e.g., 11S, 19S, and PA200; B), association of proteasome complexes with proteasome interacting partners (e.g., PKA; C), discrete subcellular locations (D), substrate preference [e.g., ubiquitin tagged vs. misfolded/denatured proteins (E) and proteasome complex stability (F)]. “X” in B, C, and E conceptually illustrates inhibition of a particular pathway or process governed by the presence or absence of PTMs on proteasomes. PIP, proteasome-interacting proteins.
