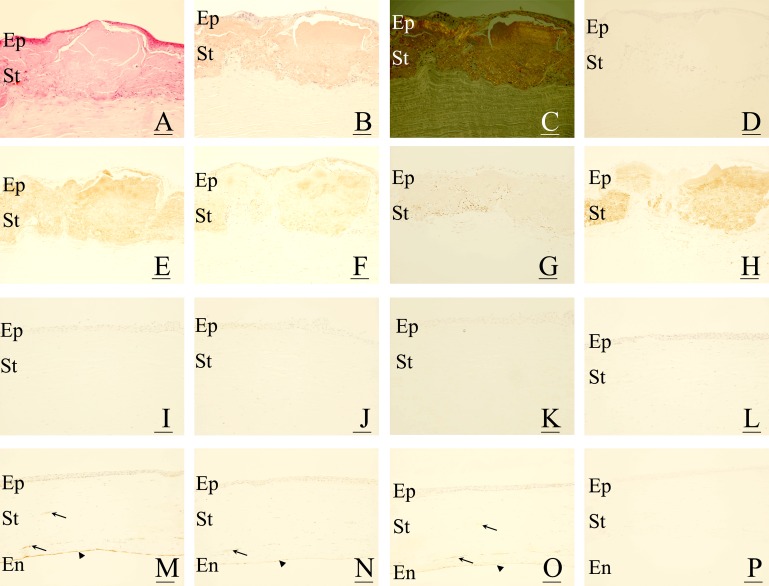
Figure 1.
Immunohistochemical localisation of advanced glycation end products (AGE) and d-β-aspartic acid-containing proteins in gelatinous drop-like corneal dystrophy (GDLD). In corneas with GDLD (A–H), eosinophilic and abnormal accumulation of proteins is seen in the superficial layers (A). The accumulated proteins contain amyloid fibrils, which are positive for Congo-red staining (1B) with birefringence (C). The accumulated proteins are positive for AGE, including Nɛ-(carboxy)methyl-l-lysine (CML) (E), pyrraline (F) and pentosidine (G), and d-β-aspartic acid-containing proteins (H). No staining was observed in negative controls (D). In corneas with bullous keratopathy (I–L), no immunoreaction against AGE, including CML (I), pyrraline (J) and pentosidine (K), and d-β-aspartic acid-containing proteins (L), was seen in the corneal stroma. In corneas with interstitial keratitis (M–P), AGE, including CML (M), pyrraline (N) and pentosidine (O), were positive in blood vessels (arrows in M–O) as well as in the corneal endothelial cells (arrowheads in M–O). In contrast, no immunoreactivity against d-β-aspartic acid-containing proteins was seen in corneas with interstitial keratitis (P). For all figures, bar = 50 μm. En, corneal endothelium; Ep, corneal epithelium; St, corneal stroma.