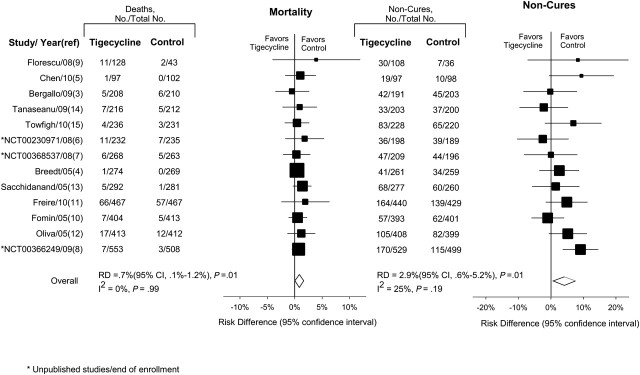
Figure 2.
Mortality and noncure rates using RD. The size of data markers is proportional to the inverse variance of each point estimate. RR, another commonly used summary statistic, was examined to test the consistency of the above findings. Tigecycline versus comparator antibiotics was associated with a significant 30% increase in mortality rates (RR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.02–1.65; P = .04) and a significant 12% increase in c-mITT noncure (RR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.02–1.23; P = .02). Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; RD, risk difference; RR, relative risk.