Figure 1. Modulation of RNAi activity in eukaryotes at different levels.
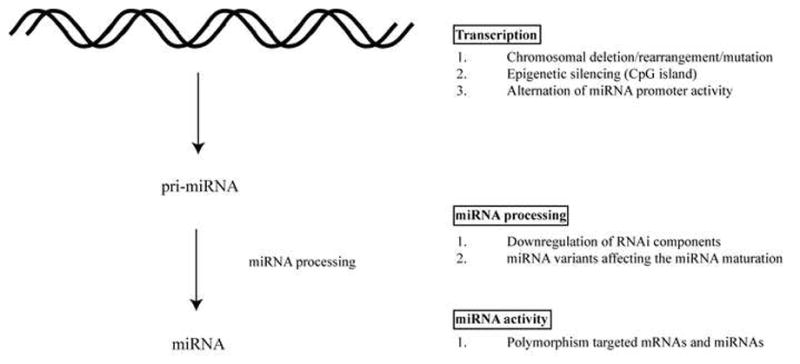
A) miRNAs are processed from precursor pri-, pre-, miRNA that contain stem-loop structure. The genes encoding miRNAs are regulated by their own promoters and regulatory elements (70, 71). The expression levels of miRNA precursor can be regulated at the transcriptional level by (1) Chromosomal deletion or translocation of regions containing miRNA genes. (2) Epigenetic silencing of regions containing miRNAs. (3) Alteration in the miRNA promoter activity. B) Functional miRNAs require a series of processing steps. (1) Downregulation of the RNAi components including Dicer, Drosha, Exportin 5, TRBP and Ago2 impairs the miRNA maturation process and has been correlated with cancer development (14–21). (2) miRNA structural variants with sequence changes at the processing-cleavage sites affect the ribonuclease activity of Drosha and Dicer (72). C) Mutations associated with sequence changes in miRNAs and miRNA target sites can affect the effectiveness of the gene silencing activity. (1) Polymorphisms, including SNP and potential deaminations of miRNAs and their targeted mRNAs have been detected in various cancers (73).
