Figure 1. Histological examination of cecal tissue.
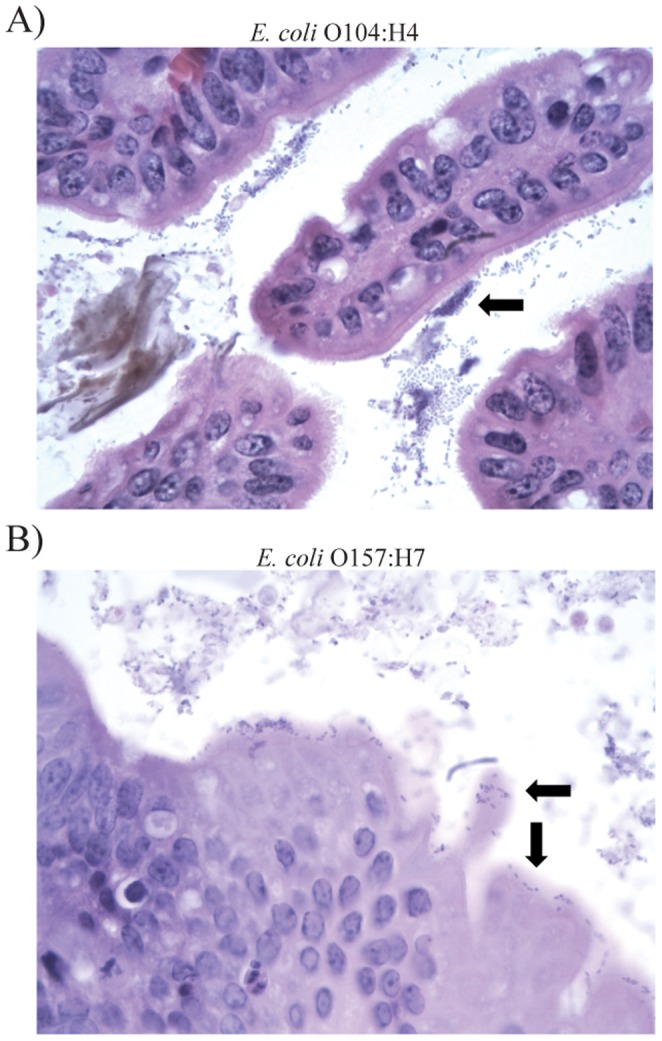
Arrows highlight A) bacterial aggregation associated with the mucus layer in the cecum of E. coli O104:H4-infected mouse 11–272, and B) bacteria associated with the cecal mucosa in E. coli O157:H7-infected mouse 11–437. Cells were stained with hematoxylin and eosin and magnified 1000x.
