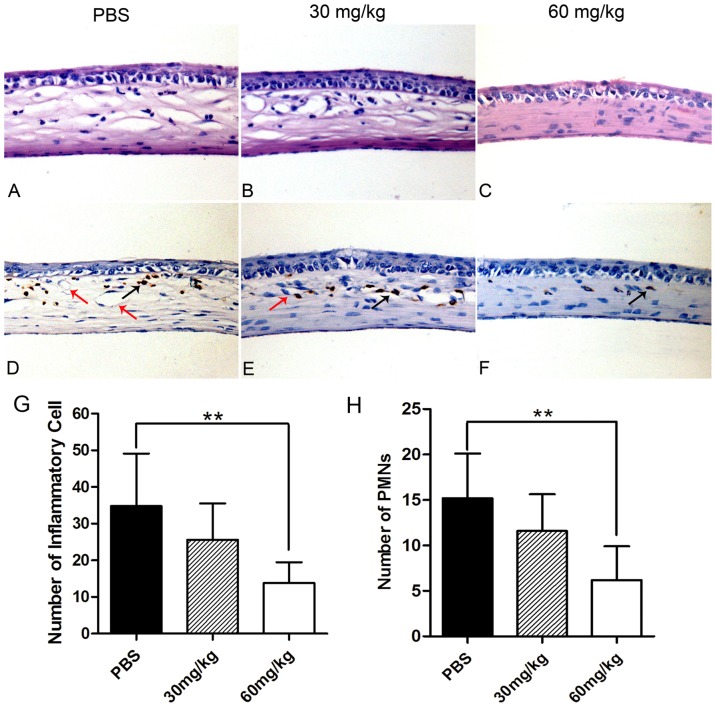
Figure 3. Anti-inflammatory effects of minocycline on the burned corneas at day 14.
(A–C) H–E staining of the mice cornea. (Magnification, ×400) The corneal thickness was increased in the control group and the low-dosage group than that in the high-dosage group. The number of infiltrated inflammatory cells in one field was lower in the corneal stroma of the high-dosage group (13.8±5.7) than that in the control group (34.8±14.3) (G). (D–F) Immunohistochemistrical staining of PMNs. The PMNs were labeled in brown and the endothelium of corneal vessels was labeled with red arrows. The number of infiltrated PMNs (black arrows) in one field was lower in the corneal stroma of the high-dosage group (6.2±3.7) than that of the control group (15.2±5.0). There were no statistical differences of inflammatory cells or PMNs between low-dosage group and control group (H). (*p<0.05).