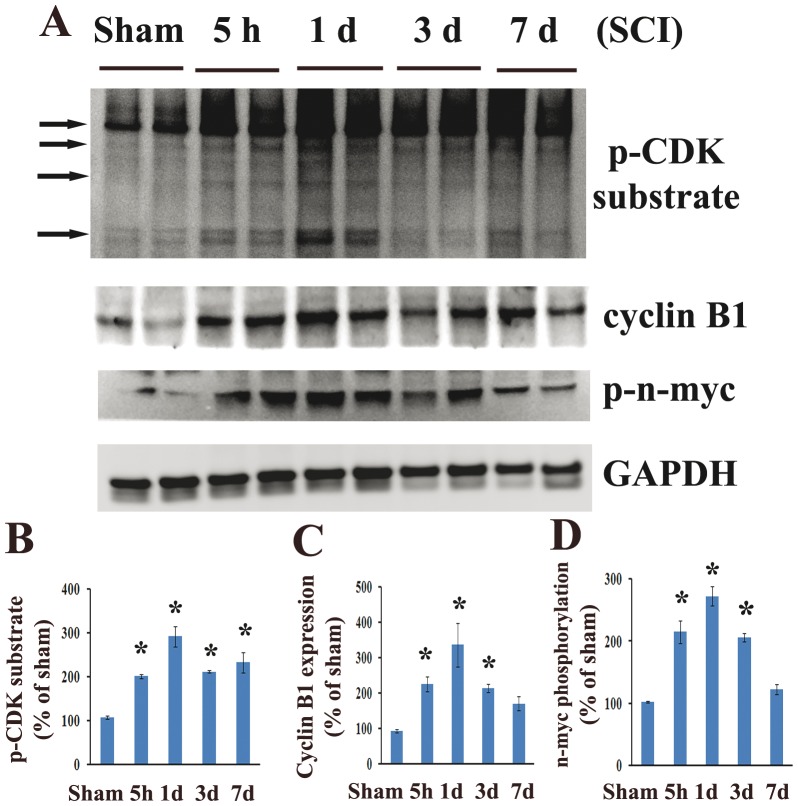
Figure 2. CDK1 activity is increased after spinal cord injury.
Western blotting analysis of common CDK substrates, CDK1 co-activator cyclin B1 and phosphorylations of specific CDK1 substrate (Ser54)-n-myc was performed in homogenates obtained from intact and injured spinal cord. A. Cyclin B1 expression was upregulated at all time points tested. Phosphorylation (Ser54) of n-myc and phospho-CDK substrate motif signal levels were increased from 5 h to day 7. B–D. Quantification of respective western blots in panel A. n = 4 rats/time point. *P<0.05 vs sham group.