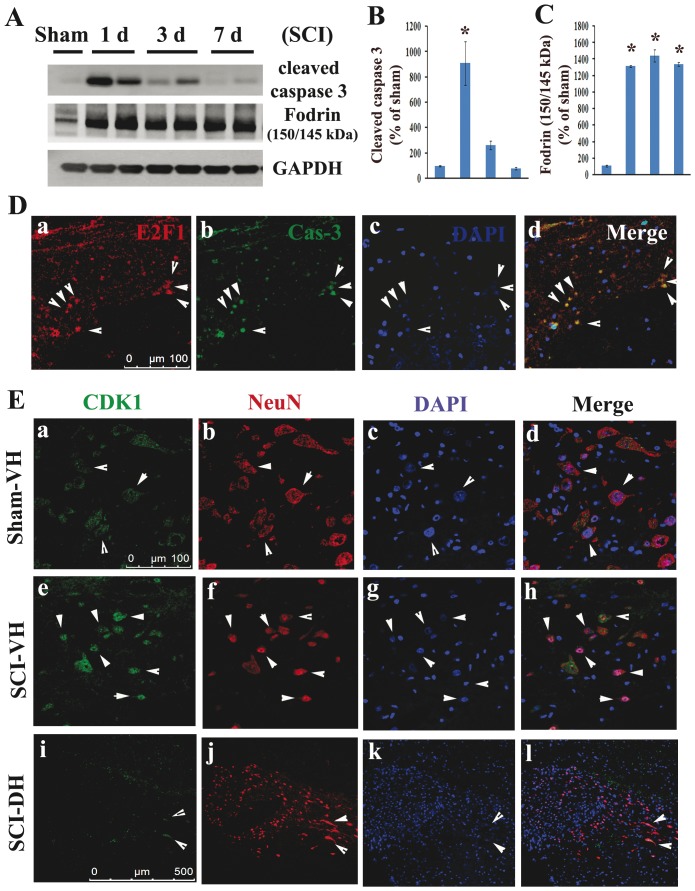
Figure 5. Colocalization of E2F1/CDK1 upregulation with neuronal apoptosis in injured spinal cord.
A–C. Western blot analysis shows a significant increase in biochemical markers of apoptosis, active caspase-3 signal, as well as 145/150 kDa cleavage product of α-fodrin after SCI. N = 4 rats/time points. *p<0.05 vs sham group. D. E2F1+ cells were co-label with cleaved caspase 3 (yellow, arrow heads) in the gray matter at 2 mm rostral to the epicenter at 1 day after SCI. Scale bar = 100 µm. E. Coronal section in intact spinal cord (top panel) shows that CDK1 was expressed in the motor neurons in the ventral horn (VH). At 1 day after injury, immunoreactivity of CDK1 (middle panel, green) was increased, and highly expressed by apoptotic motor neurons (red), as shown at 2 mm rostral to epicenter. CDK1 was rarely expressed by inter-neurons in the dorsal horn (DH) after SCI (bottom panel). Scale bar = 100 µm for D(a–h) and 500 µm for D(i–l).