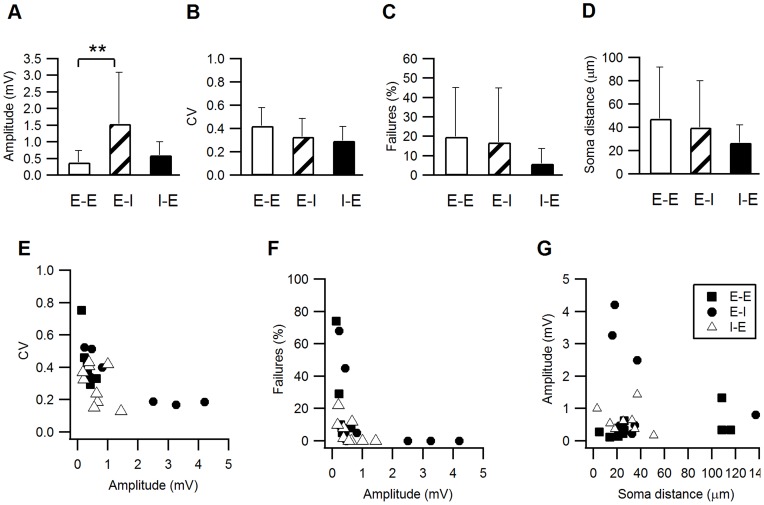
Figure 5. Variance analysis of E–E, E–I and I–E synapses.
A–C. The averaged (±s.d.) PSP amplitude (A), CV (B) and percentage failures (C) were compared among the three connection types. The EPSP amplitudes of E–I connections were significantly larger than E–E EPSPs or I–E IPSPs (p<0.05). I–E connections had on average lower CVs and percentage failures, but these were not statistically significant. D. The average horizontal distances between the pre- and postsynaptic neurons were short for all connection types: E–E 47±14, n = 10; E–I 40±14, n = 8, I–E 27±5, n = 8. E–F. The CV and percentage failures of individual synapses were plotted against their average PSP amplitude. In, general, larger PSP amplitudes were correlated with lower CVs and percentage failures and smaller PSP amplitudes correlated with the higher CVs and percentage failure. Among medium-sized PSPs no obvious correlations with the CV or percentage failures were observed. G. PSP amplitudes were plotted against the horizontal distance between the pre- and postsynaptic neurons. No correlation could be observed between these parameters (cor. Coeff. = −0.08).