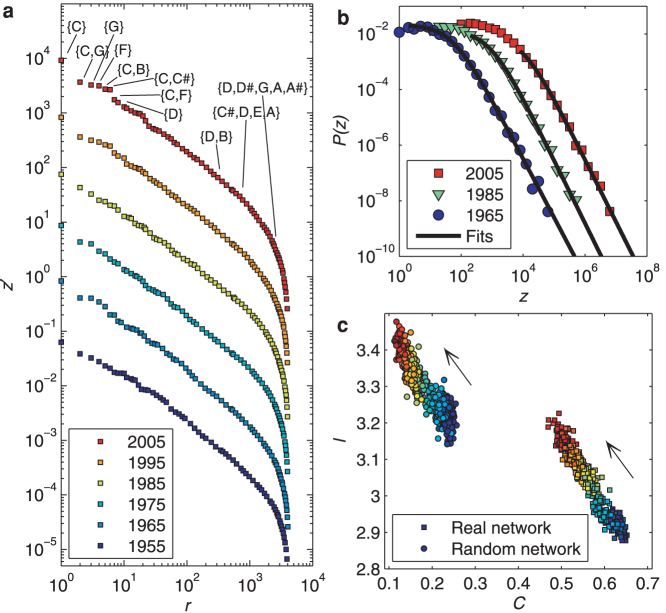
Figure 2. Pitch distributions and networks.
(a) Examples of the rank-frequency distribution (relative frequencies z′ such that 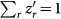 ). For ease of visualization, curves are chronologically shifted by a factor of 10 in the vertical axis. Some frequent and infrequent codewords are shown. (b) Examples of the density values and their fits, taking z as the random variable. Curves are chronologically shifted by a factor of 10 in the horizontal axis. (c) Average shortest path length l versus clustering coefficient C for pitch networks (right) and their randomized versions (left). Randomized networks were obtained by swapping pairs of links chosen at random, avoiding multiple links and self-connections. Values l and C calculated without considering the 10 highest degree nodes (see SI). Arrows indicate chronology (red and blue colors indicate values for more and less recent years, respectively).
). For ease of visualization, curves are chronologically shifted by a factor of 10 in the vertical axis. Some frequent and infrequent codewords are shown. (b) Examples of the density values and their fits, taking z as the random variable. Curves are chronologically shifted by a factor of 10 in the horizontal axis. (c) Average shortest path length l versus clustering coefficient C for pitch networks (right) and their randomized versions (left). Randomized networks were obtained by swapping pairs of links chosen at random, avoiding multiple links and self-connections. Values l and C calculated without considering the 10 highest degree nodes (see SI). Arrows indicate chronology (red and blue colors indicate values for more and less recent years, respectively).